Abstract
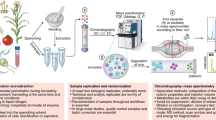
MetaboAnalyst is an integrated web-based platform for comprehensive analysis of quantitative metabolomic data. It is designed to be used by biologists (with little or no background in statistics) to perform a variety of complex metabolomic data analysis tasks. These include data processing, data normalization, statistical analysis and high-level functional interpretation. This protocol provides a step-wise description on how to format and upload data to MetaboAnalyst, how to process and normalize data, how to identify significant features and patterns through univariate and multivariate statistical methods and, finally, how to use metabolite set enrichment analysis and metabolic pathway analysis to help elucidate possible biological mechanisms. The complete protocol can be executed in ∼45 min.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fiehn, O. Metabolomics—the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant. Mol. Biol. 48, 155–171 (2002).
Wishart, D.S. Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. Trends Analyt. Chem. 27, 228–237 (2008).
Dunn, W.B. & Ellis, D.I. Metabolomics: current analytical platforms and methodologies. Trends Analyt. Chem. 24, 285–294 (2005).
Wishart, D.S. et al. HMDB: the human metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, D521–D526 (2007).
Lundberg, P. et al. MDL—The Magnetic Resonance Metabolomics Database http://mdl.imv.liu.se (European Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology, ESMRMB, 2005).
Smith, C.A. et al. METLIN—a metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug Monit. 27, 747–751 (2005).
Weljie, A.M., Newton, J., Mercier, P., Carlson, E. & Slupsky, C.M. Targeted profiling: quantitative analysis of 1H NMR metabolomics data. Anal. Chem. 78, 4430–4442 (2006).
Smith, C.A., Want, E.J., O′Maille, G., Abagyan, R. & Siuzdak, G. XCMS: processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal. Chem. 78, 779–787 (2006).
Zhao, Q., Stoyanova, R., Du, S., Sajda, P. & Brown, T.R. HiRes—a tool for comprehensive assessment and interpretation of metabolomic data. Bioinformatics 22, 2562–2564 (2006).
Xia, J., Bjorndahl, T.C., Tang, P. & Wishart, D.S. MetaboMiner—semi-automated identification of metabolites from 2D NMR spectra of complex biofluids. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 507 (2008).
Lommen, A. MetAlign: interface-driven, versatile metabolomics tool for hyphenated full-scan mass spectrometry data preprocessing. Anal. Chem. 81, 3079–3086 (2009).
Katajamaa, M., Miettinen, J. & Oresic, M. MZmine: toolbox for processing and visualization of mass spectrometry based molecular profile data. Bioinformatics 22, 634–636 (2006).
Wishart, D.S. Current Progress in computational metabolomics. Brief. Bioinform. 8, 279–293 (2007).
Cui, Q. et al. Metabolite identification via the Madison Metabolomics Consortium Database. Nat. Biotechnol. 26, 162–164 (2008).
Wishart, D.S. et al. HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D603–D610 (2009).
Henderson, J.P. et al. Quantitative metabolomics reveals an epigenetic blueprint for iron acquisition in uropathogenic Escherichia coli. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000305 (2009).
Altmaier, E. et al. Variation in the human lipidome associated with coffee consumption as revealed by quantitative targeted metabolomics. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 53, 1357–1365 (2009).
Ewald, J.C., Heux, S. & Zamboni, N. High-throughput quantitative metabolomics: workflow for cultivation, quenching, and analysis of yeast in a multiwell format. Anal. Chem. 81, 3623–3629 (2009).
Zulak, K.G., Weljie, A.M., Vogel, H.J. & Facchini, P.J. Quantitative 1H NMR metabolomics reveals extensive metabolic reprogramming of primary and secondary metabolism in elicitor-treated opium poppy cell cultures. BMC Plant Biol. 8, 5 (2008).
Xia, J., Psychogios, N., Young, N. & Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: a web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W652–W660 (2009).
Xia, J. & Wishart, D.S. MSEA: A web-based tool to identify biologically meaningful patterns in quantitative metabolomics data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, W71–W77 (2010).
Xia, J. & Wishart, D.S. MetPA: a web-based metabolomics tool for pathway analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 26, 2342–2344 (2010).
Neuweger, H. et al. MeltDB: a software platform for the analysis and integration of metabolomics experiment data. Bioinformatics 24, 2726–2732 (2008).
Kastenmuller, G., Romisch-Margl, W., Wagele, B., Altmaier, E. & Suhre, K. metaP-server: a web-based metabolomics data analysis tool. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, (2010).
Pluskal, T., Castillo, S., Villar-Briones, A. & Oresic, M. MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinformatics 11, 395 (2010).
Broeckling, C.D., Reddy, I.R., Duran, A.L., Zhao, X. & Sumner, L.W. MET-IDEA: data extraction tool for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 78, 4334–4341 (2006).
Duran, A.L., Yang, J., Wang, L.J. & Sumner, L.W. Metabolomics spectral formatting, alignment and conversion tools (MSFACTs). Bioinformatics 19, 2283–2293 (2003).
Luedemann, A., Strassburg, K., Erban, A. & Kopka, J. TagFinder for the quantitative analysis of gas chromatography—mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based metabolite profiling experiments. Bioinformatics 24, 732–737 (2008).
Wohlgemuth, G., Haldiya, P.K., Willighagen, E., Kind, T. & Fiehn, O. The Chemical Translation Service—a web-based tool to improve standardization of metabolomic reports. Bioinformatics 26, 2647–2648 (2010).
Tusher, V.G., Tibshirani, R. & Chu, G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5116–21 (2001).
Subramanian, A. et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15545–15550 (2005).
Salomonis, N. et al. GenMAPP 2: new features and resources for pathway analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 8, 217 (2007).
Goffard, N., Frickey, T. & Weiller, G. PathExpress update: the enzyme neighbourhood method of associating gene-expression data with metabolic pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W335–W339 (2009).
Hu, Z. et al. VisANT 3.5: multi-scale network visualization, analysis and inference based on the gene ontology. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W115–W121 (2009).
Goffard, N. & Weiller, G. PathExpress: a web-based tool to identify relevant pathways in gene expression data. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W176–W181 (2007).
Bijlsma, S. et al. Large-scale human metabolomics studies: a strategy for data (pre-) processing and validation. Anal. Chem. 78, 567–574 (2006).
Frolkis, A. et al. SMPDB: the small molecule pathway database. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, D480–D487 (2010).
Efron, B., Tibshirani, R., Storey, J.D. & Tusher, V. Empirical Bayes analysis of a microarray experiment. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 96, 1151–1160 (2001).
Trygg, J. & Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 16, 119–128 (2002).
Wang, T. et al. Automics: an integrated platform for NMR-based metabonomics spectral processing and data analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 83 (2009).
Stacklies, W., Redestig, H., Scholz, M., Walther, D. & Selbig, J. pcaMethods—a bioconductor package providing PCA methods for incomplete data. Bioinformatics 23, 1164–1167 (2007).
Dieterle, F., Ross, A., Schlotterbeck, G. & Senn, H. Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 78, 4281–4290 (2006).
van den Berg, R.A., Hoefsloot, H.C., Westerhuis, J.A., Smilde, A.K. & van der Werf, M.J. Centering, scaling, and transformations: improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics 7, 142 (2006).
Pavlidis, P. Using ANOVA for gene selection from microarray studies of the nervous system. Methods 31, 282–289 (2003).
Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001).
Westerhuis, C.A. et al. Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics 4, 81–89 (2007).
Goeman, J.J., van de Geer, S.A., de Kort, F. & van Houwelingen, H.C. A global test for groups of genes: testing association with a clinical outcome. Bioinformatics 20, 93–99 (2004).
Hummel, M., Meister, R. & Mansmann, U. GlobalANCOVA: exploration and assessment of gene group effects. Bioinformatics 24, 78–85 (2008).
Aittokallio, T. & Schwikowski, B. Graph-based methods for analysing networks in cell biology. Brief Bioinform. 7, 243–255 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR) and the Alberta Ingenuity Fund (AIF; now part of Alberta Innovates—Technology Futures) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.X. and D.S.W. prepared and tested the protocol and wrote the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, J., Wishart, D. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat Protoc 6, 743–760 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.319
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.319
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.