Abstract
The immunoregulatory cytokine interleukin 10 (IL-10) is expressed mainly by T helper type 2 (TH2) cells but also by TH1 cells during chronic infection. Here we observed plasticity in the expression of IL-10 and IL-13 after chronic TH1 stimulation; furthermore, the expression of Il10 and Il13 was regulated by the transcription factor E4BP4. Chronically stimulated E4BP4-deficient (Nfil3−/−; called 'E4bp4−/−' here) TH1 cells, regulatory T cells (Treg cells) and natural killer T cells (NKT cells) had attenuated expression of IL-10 and IL-13. Enforced expression of E4bp4 initiated the production of IL-10 and IL-13 by conventional TH1 cells. E4bp4−/− TH2 cells showed impairment of IL-10 production with no effect on IL-13. Our results indicate that E4BP4 has multiple functions in controlling the plasticity of IL-13 in TH1 cells and IL-10 in TH1 cells, TH2 cells, Treg cells and NKT cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 August 2011
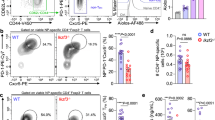
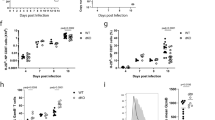
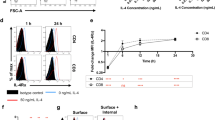
In the version of this article initially published, the text on page 455 describing the results for Figure 6d was inaccurate. The corrected text should read as follows: "...however, in response to stimulation with α-GalCer, E4bp4-/- NKT cells had no detectable IL-10 expression and lower IL-13 expression, and in response to IL-25, E4bp4-/- NKT cells had lower IL-13 expression and both wild-type and E4bp4-/- NKT cells had no detectable IL-10, whereas the expression of IFN-γ and IL-4 was unaffected (Fig. 6d)." In addition, the third column of Figure 6d should include the label 'ND' above all absent bars, and the legend should define 'ND' as 'not detected'. The errors have been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the article.
References
Murphy, K.M. & Reiner, S.L. The lineage decisions of helper T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 933–944 (2002).
Dong, C. TH17 cells in development: an updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 337–348 (2008).
Iwakura, Y., Nakae, S., Saijo, S. & Ishigame, H. The roles of IL-17A in inflammatory immune responses and host defense against pathogens. Immunol. Rev. 226, 57–79 (2008).
McKenzie, A.N. et al. Interleukin 13, a T-cell-derived cytokine that regulates human monocyte and B-cell function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 3735–3739 (1993).
Wynn, T.A. IL-13 effector functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 425–456 (2003).
Lee, G.R., Fields, P.E., Griffin, T.J. & Flavell, R.A. Regulation of the Th2 cytokine locus by a locus control region. Immunity 19, 145–153 (2003).
Wilson, C.B., Rowell, E. & Sekimata, M. Epigenetic control of T-helper-cell differentiation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 91–105 (2009).
Hayashi, N. et al. T helper 1 cells stimulated with ovalbumin and IL-18 induce airway hyperresponsiveness and lung fibrosis by IFN-γ and IL-13 production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 14765–14770 (2007).
Li, L., Xia, Y., Nguyen, A., Feng, L. & Lo, D. Th2-induced eotaxin expression and eosinophilia coexist with Th1 responses at the effector stage of lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 161, 3128–3135 (1998).
Smart, J.M. & Kemp, A.S. Increased Th1 and Th2 allergen-induced cytokine responses in children with atopic disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 32, 796–802 (2002).
Saraiva, M. & O'Garra, A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 10, 170–181 (2010).
Batten, M. et al. Cutting edge: IL-27 is a potent inducer of IL-10 but not FoxP3 in murine T cells. J. Immunol. 180, 2752–2756 (2008).
Jankovic, D. et al. Conventional T-bet+Foxp3− Th1 cells are the major source of host-protective regulatory IL-10 during intracellular protozoan infection. J. Exp. Med. 204, 273–283 (2007).
Shaw, M.H. et al. Tyk2 negatively regulates adaptive Th1 immunity by mediating IL-10 signaling and promoting IFN-γ-dependent IL-10 reactivation. J. Immunol. 176, 7263–7271 (2006).
Anderson, C.F., Oukka, M., Kuchroo, V.J. & Sacks, D. CD4+CD25−Foxp3− Th1 cells are the source of IL-10-mediated immune suppression in chronic cutaneous leishmaniasis. J. Exp. Med. 204, 285–297 (2007).
Saraiva, M. et al. Interleukin-10 production by Th1 cells requires interleukin-12-induced STAT4 transcription factor and ERK MAP kinase activation by high antigen dose. Immunity 31, 209–219 (2009).
Kuhn, R., Lohler, J., Rennick, D., Rajewsky, K. & Muller, W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75, 263–274 (1993).
Rubtsov, Y.P. et al. Regulatory T cell-derived interleukin-10 limits inflammation at environmental interfaces. Immunity 28, 546–558 (2008).
O'Shea, J.J. & Paul, W.E. Mechanisms underlying lineage commitment and plasticity of helper CD4+ T cells. Science 327, 1098–1102 (2010).
Kishikawa, H., Sun, J., Choi, A., Miaw, S.C. & Ho, I.C. The cell type-specific expression of the murine IL-13 gene is regulated by GATA-3. J. Immunol. 167, 4414–4420 (2001).
Shoemaker, J., Saraiva, M. & O'Garra, A. GATA-3 directly remodels the IL-10 locus independently of IL-4 in CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 176, 3470–3479 (2006).
Zhu, J. et al. Conditional deletion of GATA-3 shows its essential function in TH1-TH2 responses. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1157–1165 (2004).
Cowell, I.G. E4BP4/NFIL3, a PAR-related bZIP factor with many roles. Bioessays 24, 1023–1029 (2002).
Zhang, W. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of NF-IL3A, a transcriptional activator of the human interleukin-3 promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 6055–6063 (1995).
Ikushima, S. et al. Pivotal role for the NFIL3/E4BP4 transcription factor in interleukin 3-mediated survival of pro-B lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2609–2614 (1997).
Gascoyne, D.M. et al. The basic leucine zipper transcription factor E4BP4 is essential for natural killer cell development. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1118–1124 (2009).
Kamizono, S. et al. Nfil3/E4bp4 is required for the development and maturation of NK cells in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 206, 2977–2986 (2009).
Kashiwada, M. et al. IL-4-induced transcription factor NFIL3/E4BP4 controls IgE class switching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 821–826 (2010).
Lund, R., Aittokallio, T., Nevalainen, O. & Lahesmaa, R. Identification of novel genes regulated by IL-12, IL-4, or TGF-β during the early polarization of CD4+ lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 171, 5328–5336 (2003).
Lund, R. et al. Identification of genes involved in the initiation of human Th1 or Th2 cell commitment. Eur. J. Immunol. 35, 3307–3319 (2005).
Pai, S.Y., Truitt, M.L. & Ho, I.C. GATA-3 deficiency abrogates the development and maintenance of T helper type 2 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 1993–1998 (2004).
Hata, H., Yoshimoto, T., Hayashi, N., Hada, T. & Nakanishi, K. IL-18 together with anti-CD3 antibody induces human Th1 cells to produce Th1- and Th2-cytokines and IL-8. Int. Immunol. 16, 1733–1739 (2004).
Sugimoto, T. et al. Interleukin 18 acts on memory T helper cells type 1 to induce airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a naive host mouse. J. Exp. Med. 199, 535–545 (2004).
Stumhofer, J.S. et al. Interleukins 27 and 6 induce STAT3-mediated T cell production of interleukin 10. Nat. Immunol. 8, 1363–1371 (2007).
McGeachy, M.J. et al. TGF-β and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain TH-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat. Immunol. 8, 1390–1397 (2007).
Terashima, A. et al. A novel subset of mouse NKT cells bearing the IL-17 receptor B responds to IL-25 and contributes to airway hyperreactivity. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2727–2733 (2008).
Komatsu, N. et al. Heterogeneity of natural Foxp3+ T cells: a committed regulatory T-cell lineage and an uncommitted minor population retaining plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 1903–1908 (2009).
Koyanagi, M. et al. EZH2 and histone 3 trimethyl lysine 27 associated with Il4 and Il13 gene silencing in Th1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 31470–31477 (2005).
Tanaka, S. et al. The enhancer HS2 critically regulates GATA-3-mediated Il4 transcription in TH2 cells. Nat. Immunol. 12, 77–85 (2011).
Roers, A. et al. T cell-specific inactivation of the interleukin 10 gene in mice results in enhanced T cell responses but normal innate responses to lipopolysaccharide or skin irritation. J. Exp. Med. 200, 1289–1297 (2004).
Atarashi, K. et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 331, 337–341 (2011).
Zheng, W. & Flavell, R.A. The transcription factor GATA-3 is necessary and sufficient for Th2 cytokine gene expression in CD4 T cells. Cell 89, 587–596 (1997).
Grunig, G. et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 282, 2261–2263 (1998).
Walter, D.M. et al. Critical role for IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. J. Immunol. 167, 4668–4675 (2001).
Nishimura, Y. & Tanaka, T. Calcium-dependent activation of nuclear factor regulated by interleukin 3/adenovirus E4 promoter-binding protein gene expression by calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T cells and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19921–19928 (2001).
Smirnov, D.V., Smirnova, M.G., Korobko, V.G. & Frolova, E.I. Tandem arrangement of human genes for interleukin-4 and interleukin-13: resemblance in their organization. Gene 155, 277–281 (1995).
Takeda, K. et al. Essential role of Stat6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature 380, 627–630 (1996).
Mohrs, M. et al. Differences between IL-4- and IL-4 receptor α-deficient mice in chronic leishmaniasis reveal a protective role for IL-13 receptor signaling. J. Immunol. 162, 7302–7308 (1999).
Sakai, K. & Miyazaki, J. A transgenic mouse line that retains Cre recombinase activity in mature oocytes irrespective of the cre transgene transmission. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 237, 318–324 (1997).
Yagi, R. et al. The IL-4 production capability of different strains of naive CD4+ T cells controls the direction of the TH cell response. Int. Immunol. 14, 1–11 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Murphy (Washington University) for DO11.10 mice on the BALB/c background; S. Akira (Osaka University) for Stat6−/− mice; F. Brombacher (University of Cape Town) for Il4r−/− mice; C. Wilson (Washington University) for Cd4-Cre mice; R. Abe (Tokyo University of Science) for the PV-1 mAb to CD28; T. Kitamura (Tokyo University) for Platinum-E packaging cells; H. Fujimoto, Y. Suzuki, K. Ikari and E. Hayashi for technical assistance; and P. Burrows for comments on the manuscript. Supported by RIKEN (Y. Motomura), the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and the Program for Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. Motomura built the initial constructs, generated mouse lines and confirmed them in vivo, and did most of the experiments; H.K. and A.H. did microarray and bioinformatics analysis; Y. Matsunaga, K.M. and H.I. did airway hyper-responsiveness experiments; K.A. provided Il10 reporter mice; S.H. analyzed Treg cells; H.W. and M.T. analyzed NKT cells; J.Z. provided materials; and M.K. designed and coordinated experiments, supervised the project and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–10 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 1381 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motomura, Y., Kitamura, H., Hijikata, A. et al. The transcription factor E4BP4 regulates the production of IL-10 and IL-13 in CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 12, 450–459 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2020
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2020
This article is cited by
-
Cellular immunity reflects the persistent symptoms among COVID-19 recovered patients in Japan
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Current Developments in the Preclinical and Clinical use of Natural Killer T cells
BioDrugs (2023)
-
A new border for circadian rhythm gene NFIL3 in diverse fields of cancer
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)
-
Re-programming mouse liver-resident invariant natural killer T cells for suppressing hepatic and diabetogenic autoimmunity
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Dysregulation of REV-ERBα impairs GABAergic function and promotes epileptic seizures in preclinical models
Nature Communications (2021)