Abstract
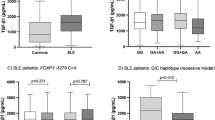
Recently, several studies have demonstrated the role of vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms in the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We aimed to evaluate VDR (ApaI, BsmI, and FokI) gene polymorphisms and haplotypes as a risk factors and/or activity markers for SLE, and whether they influence 25-hydroxyvitamin (25(OH) D) level. One hundred and seven SLE patients and 129 controls were enrolled in this study. Disease activity in SLE patients was assessed using Disease Activity Index. Polymorphisms of VDR gene were detected using polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism. Serum 25(OH) D levels were measured using ELISA. We found that ApaI AA genotype, BsmI B allele, Bb, BB genotypes, FokI F allele and FF genotype frequencies of VDR were increased in SLE group. There were significant associations of VDR ApaI AA, BsmI BB, and FokI FF genotypes with lupus nephritis and higher SLE activity scores. Moreover, serum 25(OH) D levels were increased in SLE patients carrying FokI ff genotype compared with patients carrying FF genotype. VDR haplotypes aBF and ABF were associated with SLE risk. The ABF haplotype was associated with higher SLE activity scores and lower serum 25(OH) D concentrations. We observed that the presence of leuko/lymphopenia, renal disorders, higher SLE activity scores and higher anti-dsDNA levels were accompanied by a significant decrease of serum 25(OH)D concentrations. We concluded that The VDR genes polymorphisms, haplotypes, and decreased 25(OH) D levels were associated with risk and more activity scores of SLE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manson JJ, Isenberg DA (2003) The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Neth J Med 61:343–346
Arnson Y, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Vitamin D and autoimmunity: new aetiological and therapeutic considerations. Ann Rheum Dis 66:1137–1142
Boonstra A, Barrat FJ, Crain C, Heath VL, Savelkoul HF, O’Garra A (2001) 1-Alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 has a direct effect on naive CD4(+) T cells to enhance the development of Th2 cells. J Immunol 167:4974–4980
Maruotti N, Cantatore FP (2010) Vitamin D and the immune system. J Rheumatol 37:491–495
Kamen DL, Aranow C (2008) The link between vitamin D deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 10:273–280
Costenbader KH, Feskanich D, Holmes M, Karlson EW, Benito-Garcia E (2008) Vitamin D intake and risks of systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis in women. Ann Rheum Dis 67:530–535
Baker AR, McDonnell DP, Hunghes M et al (1988) Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:3294–3298
Miyamoto K, Kesterson RA, Yamamoto H et al (1997) Structural organization of the human vitamin D receptor chromosomal gene and its promoter. Mol Endocrinol 11:1165–1179
Hitchon CA, Sun Y, Robinson DB, Peschken CA, Bernstein CN, Siminovitch KA, El-Gabalawy HS (2012) Vitamin D receptor polymorphism rs2228570 (Fok1) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in North American natives. J Rheumatol 39(9):1792–1797
Mohammad Nejad Z, Ghanbari M, Ganjali R, Afshari JT, Heydarpour M, Taghavi SM, Fatemi S, Rafatpanah H (2012) Association between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and type 1 diabetes mellitus in Iranian population. Mol Biol Rep 39(2):831–837
Ozaki Y, Nomura S, Nagahama M, Yoshimura C, Kagawa H, Fukuhara S (2000) Vitamin-D receptor genotype and renal disorder in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nephron 85:86–91
Sakulpipatsin W, Verasertniyom O, Nantiruj K, Totemchokchyakarn K, Lertsrisatit P, Janwityanujit S (2006) Vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphisms in Thai patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R48
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A Disease Activity Index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35:630–640
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 357:266–281
Niino M, Fukazawa T, Yabe I, Kikuchi S, Sasaki H, Tashiro K (2000) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in multiple sclerosis and the association with HLA class II alleles. J Neurol Sci 177(1):65–71
Sainz J, Van Tornout JM, Loro ML, Sayre J, Roe TF, Gilsanz V (1997) Vitamin D-receptor gene polymorphisms and bone density in prepubertal American girls of Mexican descent. N Engl J Med 337(2):77–82
Yasovanthi J, Venkata Karunakar K, Sri Manjari K, Pulla Reddy B, Ajeya Kumar P, Sesha Charyulu M, Aruna P, Narasimulu G, Jyothy A (2011) Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with BMD and their effect on 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 levels in pre- and postmenopausal South Indian women from Andhra Pradesh. Clin Chim Acta 412(7–8):541–544
Rosen CJ (2011) Vitamin D insufficiency. N Engl J Med 364:248–254
Hollis BW (2005) Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels indicative of vitamin D sufficiency: implications for establishing a new effective dietary intake recommendation for vitamin D. J Nutr 135:317–322
Sullivan KE (2000) Genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical implications. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 26:229–256
Luo XY, Yang MH, Wu FX, Wu LJ, Chen L, Tang Z, Liu NT, Zeng XF, Guan JL, Yuan GH (2012) Vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphism B allele, but not BB genotype, is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Han Chinese population. Lupus 21(1):53–59
Monticielo OA, Brenol JC, Chies JA, Longo MG, Rucatti GG, Scalco R et al (2012) The role of BsmI and FokI vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in Brazilian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 21(1):43–52
Valdivielso JM, Fernandez E (2006) Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and diseases. Clin Chim Acta 371:1–12
O’Regan S, Chesney RW, Hamstra A, Eisman JA, O’Gorman AM, Deluca HF (1979) Reduced serum 1,25-(OH)2 vitamin D3 levels in prednisone-treated adolescents with systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Paediatr Scand 68:109–111
Kamen DL, Cooper GS, Bouali H, Shaftman SR, Hollis BW, Gilkeson GS (2006) Vitamin D deficiency in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 5:114–117
Damanhouri LH (2009) Vitamin D deficiency in Saudi patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Saudi Med J 30:1291–1295
Toloza SM, Cole DE, Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2010) Vitamin D insufficiency in a large female SLE cohort. Lupus 19:13–19
Luo XY, Wu LJ, Chen L, Yang MH, Liao T, Liu NT, Ku-Er B, Xie CM, Shi RG, Tang Z, Zhao Y, Zeng XF, Yuan GH (2012) The association of vitamin D receptor gene ApaI and BsmI polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 51(2):131–135
Garcia-Lozano JR, Gonzalez-Escribano MF, Valenzuela A, Garcia A, Nunez-Roldan A (2001) Association of vitamin D receptor genotypes with early onset rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunogenet 28:89–93
Mostowska A, Lianeri M, Wudarski M, Olesińska M, Jagodziński PP (2013) Vitamin D receptor gene BsmI, FokI, ApaI and TaqI polymorphisms and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Biol Rep 40(2):803–810
Huang CM, Wu MC, Wu JY, Tsai FJ (2002) Association of vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphisms in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 11:31–34
Lee YH, Bae SC, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2011) Associations between vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 38:3643–3651
Abbasi M, Rezaieyazdi Z, Afshari JT, Hatef M, Sahebari M, Saadati N (2010) Lack of association of vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphisms in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int 30:1537–1539
Zmuda JM, Cauley JA, Ferrell RE (2000) Molecular epidemiology of vitamin D receptor gene variants. Epidemiol Rev 22:203–217
Luo XY, Wu LJ, Yang MH, Liu NT, Liao T, Tang Z et al (2011) Relationship of vitamin D receptor gene FokI polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 27(8):901–905
Huang CM, Wu MC, Wu JY, Tsai FJ (2002) No association of vitamin D receptor gene start codon fok 1 polymorphisms in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 29(6):1211–1213
Morrison NA, Qi JC, Tokita A et al (1994) Prediction of bone density from vitamin D receptor alleles. Nature 20(367):284–287
McGrath JJ, Saha S, Burne TH, Eyles DW (2010) A systematic review of the association between common single nucleotide polymorphisms and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 121:471–477
Orton SM, Morris AP, Herrera BM et al (2008) Evidence for genetic regulation of vitamin D status in twins with multiple sclerosis. Am J Clin Nutr 88:441–447
Smolders J, Damoiseaux J, Menheere P, Tervaert JW, Hupperts R (2009) Fok-I vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism (rs10735810) and vitamin D metabolism in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 207:117–121
Engelman CD, Fingerlin TE, Langefeld CD et al (2008) Genetic and environmental determinants of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels in Hispanic and African Americans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3381–3388
Wjst M, Altmuller J, Faus-Kessler T, Braig C, Bahnweg M, Andre E (2006) Asthma families show transmission disequilibrium of gene variants in the vitamin D metabolism and signalling pathway. Respir Res 7:60
Abrams SA, Griffin IJ, Hawthorne KM et al (2005) Vitamin D receptor Fok1 polymorphisms affect calcium absorption, kinetics, and bone mineralization rates during puberty. J Bone Miner Res 20:945–953
Abbas S, Nieters A, Linseisen J, Slanger T, Kropp S, Mutschelknauss EJ, Flesch-Janys D, Chang-Claude J (2008) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and haplotypes and postmenopausal breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res 10(2):31
Acikbas I, Sanlı B, Tepeli E, Ergin S, Aktan S, Bagci H (2012) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and haplotypes (ApaI, BsmI, FokI, TaqI) in Turkish psoriasis patients. Med Sci Monit 18(11):661–666
Morrison NA, Yeoman R, Kelly PJ, Eisman JA (1992) Contribution of trans-acting factor alleles to normal physiological variability: vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and circulating osteocalcin. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:6665–6669
Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, Van Meurs JB, Pols HA, Van Leeuwen JP (2004) Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene 338:143–156
Arai H, Miyamoto K-I, Taketani Y, Yamamoto H, Iemori Y, Morita K, Tonai T, Nishisho T, Mori S, Takeda E (1997) A vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in the translation initiation codon: effect on protein activity and relation to bone mineral density in Japan women. J Bone Miner Res 12:915–921
Yeap SS, Othman AZ, Zain AA, Chan SP (2012) Vitamin D levels: its relationship to bone mineral density response and disease activity in premenopausal Malaysian systemic lupus erythematosus patients on corticosteroids. Int J Rheum Dis 15:17–24
Hamza RT, Awwad KS, Ali MK, Hamed AI (2011) Reduced serum concentrations of 25-hydroxy vitamin D in Egyptian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: relation to disease activity. Med Sci Monit 17:711–718
Mok CC, Birmingham DJ, Ho LY, Hebert LA, Song H, Rovin BH (2012) Vitamin D deficiency as marker for disease activity and damage in systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison with anti-dsDNA and anti-C1q. Lupus 21:36–42
Mok CC, Birmingham DJ, Leung HW, Hebert LA, Song H, Rovin BH (2012) Vitamin D levels in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship with disease activity, vascular risk factors and atherosclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:644–652
Amital H, Szekanecz Z, Szu¨cs G, Danko′ K, Nagy E, Cse′pa′ny T, Kiss E, Rovensky J, Tuchynova A, Kozakova D, Doria A, Corocher N, Agmon-Levin N, Barak V, Orbach H, Zandman-Goddard G, Shoenfeld Y (2010) Serum concentrations of 25-OH vitamin D in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are inversely related to disease activity: is it time to routinely supplement patients with SLE with vitamin D? Ann Rheum Dis 69:1155–1157
Bogaczewicz J, Sysa-Jedrzejowska A, Arkuszewska C, Zabek J, Kontny E, McCauliffe D, Wozniacka A (2012) Vitamin D status in systemic lupus erythematosus patients and its association with selected clinical and laboratory parameters. Lupus 21:477–484
Lemire JM, Ince A, Takashima M (1992) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates the expression of experimental murine lupus of MRL/l mice. Autoimmunity 12:143–148
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emerah, A.A., El-Shal, A.S. Role of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level in Egyptian female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Biol Rep 40, 6151–6162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2726-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2726-9