Abstract
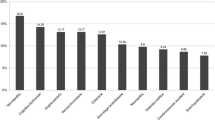
The goals of this study were to ascertain damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) from five rheumatologic centres in Argentina and to examine overall damage, damage by domain and damage by item within each domain. We performed a retrospective observational study including patients with SLE (ACR 1997 revised and modified criteria) from five rheumatology centres in Argentina. Organ damage was scored using the SLICC/ACR DI (SDI), ascertained at years 1, 2, 5 and 10. Three centres provided information up to the fifth year. Of the 197 patients, 88.3% were women and their mean age was 33.2 years. The mean disease duration and follow-up were 7.6 and 5.3 years, respectively. Damage accrued gradually over time with SDI ranging from 0.52 (±1.1) at year 1 up to 2.46 (±2.1) at year 10. The renal system was the most involved system, followed by the neuropsychiatric, the cardiovascular and the musculoskeletal systems. Proteinuria, cognitive impairment, pericarditis, avascular necrosis, cataract and alopecia were the predominant items in their respective systems. Systems such as peripheral vascular, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, diabetes, malignancy and premature gonadal failure were not frequent. Overall SDI had a gradual increase over time. Damage in each domain of SDI, except for diabetes, had a similar behaviour. Behaviour of items in each domain varied.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mills JA (1994) Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 330:1871–1879
Boumpas DT, Fessler BJ, Austin HA 3rd et al (1995) Systemic lupus erythematosus: emerging concepts. Part 2: dermatologic and joint disease, the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome, pregnancy and hormonal therapy, morbidity and mortality, and pathogenesis. Ann Intern Med 123:42–53
Abu-Shakra M, Urowitz MB, Gladman DD et al (1995) Mortality studies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Results from a single center I. Cause of death. J Rheumatol 22:1259–1264
Urowitz MB, Gladman DD, Abu-Shakra M et al (1997) Mortality studies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Results from a single center. III. Improved survival over 24 years. J Rheumatol 24:1061–1065
Urowitz MB, Bookman AA, Koehler BE et al (1976) The bimodal mortality pattern of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med 60:221–225
Rubin LA, Urowitz MB, Gladman DD et al (1985) Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: the bimodal pattern revisited. Q J Med 55:87–98
Gladman DD (1993) Indicator of disease activity, prognosis, and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 5:587–595
Gladman DD, Goldsmith CH, Urowitz MB et al (2000) The Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/ACR of Rheumatology (SLICC/ACR) Damage Index for systemic lupus erythematosus international comparison. J Rheumatol 27:373–376
Fortin PR, Feland D, Clarke AE et al (1997) Activity and damage predict later flares in lupus. Arthritis Rheum 40(Suppl 9):S207 (Abstract)
Stoll T, Seifert B, Isemberg DA (1996) SLICC/ACR Damage Index is valid, and renal and pulmonary organ scores are predictors of severe outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol 35:248–254
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Gladman DD, Ginzler E, Goldsmith C et al (1996) The development and initial validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 39(3):363–369
Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Goldsmith CH et al (1997) The reliability of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(5):809–813
Zonana-Nacach A, Camargo-Coronel A, Yanez P et al (1998) Measurement of damage in 210 Mexican patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship with disease duration. Lupus 7(2):119–123
Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Rahman P et al (2003) Accrual of organ damage over time in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 30(9):1955–1959
Alarcón GS, McGwin G Jr, Bartolucci AA et al (2001) Systemic lupus erythemtosus in three ethnic groups. IX. Differences in damage accrual. Arthritis Rheum 44(12):2797–2806
Nossent JC (1998) SLICC/ACR Damage Index in Afro-Caribbean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: change and relationship to disease activity, corticosteroid therapy and prognosis. J Rheumatol 25:654–659
Petri M (1996) Accrual of organ damage in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 39(Suppl 21):S261 (Abstract)
Stoll T, Sutcliffe N, Mach J et al (2004) Analysis of the relationship between disease activity and damage in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus—a 5-yr prospective study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:1039–1044
Rivest C, Lew RA, Welsing PM et al (2000) Association between clinical factors, socioeconomic status, and organ damage in recent onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 27:680–684
Yee CS, Hussein H, Skan J et al (2003) Association of damage with autoantibody profile, age, sex, and disease duration in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 42(2):276–279
Nived O, Jonsen A, Bengtsson AA et al (2002) High predictive value of Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for survival in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 29(7):1398–1400
Manger K, Manger B, Repp R et al (2002) Definition of risks factors for death, end renal disease, and thromboembolic events in monocentric cohort of 338 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 61(12):1065–1070
Rahman P, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB et al (2001) Early damage as measured by the SLICC/ACR Damage Index is a predictor of mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 10(2):93–96
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Egurbide MV, Ugalde J et al (2004) High impact of antiphopholipid syndrome on irreversible organ damage and survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med 164:77–82
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Raul Galoppe, Ph.D. (Montclair State University) for his help in translating the manuscript. The authors also express their sincere gratitude to Dr. Graciela Alarcon for the critical review of the manuscript. Acknowledgment is also given to Elena Carrera and Liliana Contini (Unidad de Biometría, Facultad de Bioquímica y Ciencias Biológicas, Santa Fe) for their assistance with the statistics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassano, G., Roverano, S., Paira, S. et al. Accrual of organ damage over time in Argentine patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a multi-centre study. Clin Rheumatol 26, 2017–2022 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0604-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0604-3