Abstract
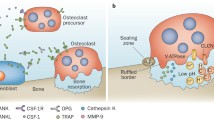
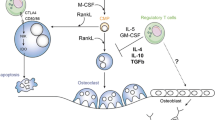
Osteoclasts, which are present only in bone, are multinucleated giant cells with the capacity to resorb mineralized tissues. These osteoclasts are derived from hemopoietic progenitors of the monocyte-macrophage lineage. Osteoblasts are involved in osteoclastogenesis through a mechanism involving cell-to-cell contact with osteoclast progenitors. The recent discovery of osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF)/receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF)-ΚB ligand (RANKL) allowed elucidation of the precise mechanism by which osteoblasts regulate osteoclastic bone resorption. Synovial fibroblasts and activated T lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis also express RANKL, which appears to trigger bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis as well. Recent studies have shown that T lymphocytes produce cytokines other than RANKL, such as interleukin (IL)-17, granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interferon (IFN)-Γ, which have powerful regulatory effects on osteoclastogenesis. The possible roles of RANKL and other cytokines produced by T lymphocytes in osteoclast differentiation are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Udagawa, N. The mechanism of osteoclast differentiation from macrophages: possible roles of T lymphocytes in osteoclastogenesis. J Bone Miner Metab 21, 337–343 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-003-0439-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-003-0439-1