Abstract
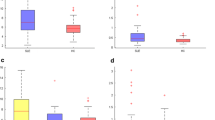
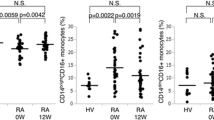
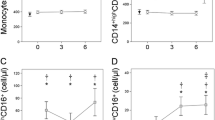
Most human peripheral blood monocytes strongly express surface CD14, but not CD16 (CD14++/CD16–). A smaller group of monocytes express lower levels of CD14 and also express CD16 (CD14+/CD16+). This subgroup has different functional characteristics and is expanded in a number of disease states. We aimed to determine the percentage of circulating CD14+/CD16+ monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and relate this to disease measures. Peripheral blood was sampled from 31 SLE patients, 19 rheumatoid arthritis patients, and 19 healthy controls. The percentage of CD14+/CD16+ monocytes was determined by immunofluorescence labelling and dual colour flow cytometry. The percentage of CD14+/CD16+ monocytes was significantly lower in rheumatoid arthritis (median 4.90%) than in normal subjects (median 7.30%, P=0.014),and in rheumatoid arthritis than in SLE patients (median 9.40%, P=0.009). The percentage of CD14+/CD16+ monocytes in SLE was not significantly different from that in healthy subjects. This lower percentage of CD14+/CD16+ monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis may be important in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cairns, A.P., Crockard, A.D. & Bell, A.L. The CD14+ CD16+ monocyte subset in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int 21, 189–192 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-001-0165-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-001-0165-8