Abstract
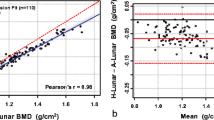
Many studies have shown the high correlation between Lunar and Hologic DXA bone mineral density (BMD) measurements despite differences in absolute calibration. However, in clinical practice, raw BMD values (in g/cm2) are not normally used for assessing skeletal status and fracture risk. Instead, the BMD values are expressed in terms of the number of standard deviations above or below the young normal value (commonly referred to as theT-score). If the normative populations of the various systems are consistent, the standard deviation scores should also be consistent. For this reason, the World Health Organization (WHO) recently established diagnostic criteria for osteoporosis based onT-scores and not BMD. However, few studies have compared the instruments in terms of their standard deviation scores. In this study, we used linear regression to compareT-scores in 83 women at L1–4 and 120 women at the femoral neck obtained on a Lunar DPX and a Hologic QDR-1000/W system. Patient BMD andT-score measurements were highly correlated between the two systems (r>0.95). No clinically significant difference in L1–4T-scores was seen (less than 0.1 SD). However, linear regression analysis confirmed a systematic difference of 0.9 SD between the femoral neck T-scores. This discrepancy is caused by: (1) differences in the normal populations, and (2) differences in statistical models used to determine the young normal mean and standard deviation. In an attempt to correct the discrepancy, the female young normal mean and standard deviation were recalculated for the femoral neck using published epidemiological data from NHANES and existing DXA cross-calibration equations. The Hologic young normal value (mean ± SD) was redefined as 0.85±0.11 g/cm2, while the Lunar value was redefined as 1.00±0.11 g/cm2. When the femoral neckT-scores for the study population were recalculated on the basis of these new values, the results were equivalent between manufacturers, effectively eliminating the discrepancy. However, the revised values should be confirmed by additional measurements in young normal adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Consensus development conference: prophylaxis and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med 1991;90:107–10.
Consensus development conference. Diagnosis, prophylaxis and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med 1993;94:646–50.
Kanis JA, Melton LJ III, Christiansen C, Johnston CC, Khaltaev N. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 1994;9:1137–41.
Pouilles JM, Tremollieres F, Ribot C. Spine and femur densitometry at the menopause: are both sites necessary in the assessment of the risk of osteoporosis? Calcif Tissue Int 1993;52:344–7.
Lai K, Rencken M, Drinkwater BL, Chesnut CH III. Site of bone density measurement may affect therapy decision. Calcif Tissue Int 1993;53:225–8.
Genant HK, Grampp S, Glueer CC, Faulkner KG, Jergas M, Engelke K, et al. Universal standardization for dual x-ray absorptiometry: patient and phantom cross-calibration results. J Bone Miner Res 1994;9:1503–14.
Pocock NA, Sambrook PN, Nguyen T, Kelly P, Freund J, Eisman JA. Assessment of spinal and femoral bone density by dual x-ray absorptiometry: comparison of Lunar and Hologic instruments. J Bone Miner Res 1992;7:1081–4.
Looker AC, Wahner HW, Dunn WL, Calvo MS, Harris TB, Heyse SP, et al. Proximal femur bone mineral levels of US adults. Osteoporosis Int 1995;5:389–409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faulkner, K.G., Roberts, L.A. & McClung, M.R. Discrepancies in normative data between Lunar and Hologic DXA systems. Osteoporosis Int 6, 432–436 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01629574
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01629574