Article Text
Abstract
Objectives The prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases who are frequently treated with disease modifying therapies remains poorly understood. This meta-analysis aims to assess the prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in autoimmune diseases.
Methods Electronic databases were searched for observational and case–controlled studies. We sorted medications into glucocorticoids, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs (b/tsDMARDs), which was also divided into monotherapy and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy.
Results We analysed 62 observational studies with a total of 319 025 patients with autoimmune diseases. The prevalence of COVID-19 was 0.011 (95% CI: 0.005 to 0.025). Meta-analysis of seven case–controlled studies demonstrated that the risk of COVID-19 in autoimmune diseases was significantly higher than in control patients (OR: 2.19, 95% CI: 1.05 to 4.58, p=0.038). Meta-regression analysis showed glucocorticoids were significantly associated with the risk of COVID-19. For clinical outcomes, we assessed 65 studies with 2766 patients with autoimmune diseases diagnosed with COVID-19. The rates of hospitalisation and mortality were 0.35 (95% CI: 0.23 to 0.50) and 0.066 (95% CI: 0.036 to 0.12), respectively. Glucocorticoids, csDMARDs and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy increased the risk of these outcomes, whereas b/tsDMARDs monotherapy, particularly antitumour necrosis factor agents, were associated with a lower risk of hospitalisation and death.
Conclusions Our meta-analysis demonstrated that patients with autoimmune diseases had an increased risk of COVID-19, primarily attributed to glucocorticoid use. b/tsDMARDs monotherapy was associated with a lower risk of severe COVID-19 suggesting its safety in the COVID-19 pandemic.
- autoimmune diseases
- rheumatoid arthritis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- biological therapy
- psoriasis
- inflammatory bowel disease
This article is made freely available for use in accordance with BMJ’s website terms and conditions for the duration of the covid-19 pandemic or until otherwise determined by BMJ. You may use, download and print the article for any lawful, non-commercial purpose (including text and data mining) provided that all copyright notices and trade marks are retained.
https://bmj.com/coronavirus/usageStatistics from Altmetric.com
- autoimmune diseases
- rheumatoid arthritis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- biological therapy
- psoriasis
- inflammatory bowel disease
Key messages
What is already known about this subject?
The prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases who are frequently treated with immunosuppressive or anticytokine drugs remains poorly understood.
What does this study add?
The prevalence of COVID-19 in autoimmune diseases was 0.011 (95% CI: 0.005 to 0.025) which was significantly higher than in the comparator population.
Glucocorticoids increased the risk of COVID-19 and its severe outcomes.
Conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs (b/tsDMARDs)–csDMARDs combination therapy significantly increased the risk of severe outcomes, whereas b/tsDMARDs monotherapy, in particular anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy, reduced the risk of severe COVID-19.
How might this impact on clinical practice or future developments?
Unlike glucocorticoids, csDMARDs and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy, b/tsDMARDs monotherapy can be safely used during COVID-19 pandemic.
Introduction
The outbreak of COVID-19 caused by the novel SARS-CoV-2 has spread worldwide leading to large number of infections and deaths.1 Patients with autoimmune diseases (ADs) are frequently treated with immunosuppressive or anticytokine drugs, which raises concern for infectious complications, placing patients and physicians at a crossroads with respect to continuation or cessation of these disease modifying therapies.
To understand the incidence and prognosis of COVID-19 in ADs, international registries of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (SECURE-IBD registry2) or rheumatic diseases (C19-GRA3) diagnosed with COVID-19 have been developed and analysed their COVID-19 outcomes. These data have demonstrated that similar to the general population, age and underlying comorbidities are poor prognostic factors of COVID-19 in ADs.4 In terms of treatments, both registries demonstrated that patients treated with glucocorticoids (GCs) had poor clinical outcomes of COVID-19, whereas those treated with antitumour necrosis factor (TNF) therapies, particularly when used as a monotherapy, had a decreased risk of hospitalisation due to COVID-19.2 3 These findings suggest that anti-TNF monotherapy may be protective against severe COVID-19. However, each study or registry has a limited sample size. Therefore, there is a need to integrate findings across studies to better understand the risk of COVID-19 in ADs.
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the prevalence of COVID-19 and investigate its clinical outcomes in ADs. We also assessed how individual risk factors, including comorbidities and medical therapies, influence the prevalence and clinical outcomes in ADs.
Methods
Search strategy and study selection
This meta-analysis was conducted according to a priori defined protocol that is in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guideline.5 The protocol of this meta-analysis has been submitted to the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews.6 We searched PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, EMBASE, medRxiv (https://www.medrxiv.org/) from inception to 31 July 2020 to identify studies assessing the prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in ADs.
As for inclusion criteria, we considered observational or case–controlled studies reporting the prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in ADs. There were no restrictions regarding age, sex or duration of the study. We imposed no geographic or language restrictions. Three authors (SA, SH and AS) independently screened each of the potential studies to determine whether they were eligible for inclusion. Areas of disagreement or uncertainty were resolved by consensus among the authors. Studies were identified with the following terms: ‘COVID-19’, ‘inflammatory bowel disease’, ‘psoriasis’, ‘rheumatic diseases’, ‘systemic lupus erythematosus’ and ‘autoimmune diseases’.
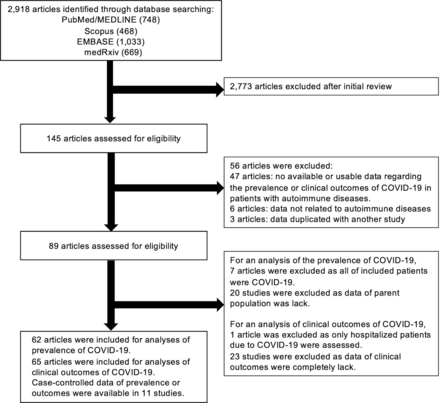
Single case reports were excluded. Given several studies used initial data from C19-GRA registry, we included a study with data of the first 600 patients submitted to C19-GRA registry3 and excluded other studies with preliminary data.7–9 For an analysis for the prevalence of COVID-19, studies in which all of included patients were COVID-19 were excluded. As for clinical outcomes of COVID-19, studies that included only hospitalised or deceased patients were excluded. The search strategy is described in figure 1.
Flow chart of the assessment of the studies identified in the meta-analysis.
Data extraction and quality assessment
All data were independently abstracted in duplicate by two authors (SA and AS) by using a data extraction form. Data on the study characteristics, such as author name, year of publication, study design, duration, study location, sample size, diagnosis of ADs, type of medications, age and gender of patients, comorbidities including hypertension, diabetes and obesity, prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 were collected. We rated the quality of evidence according to the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach to assess the certainty of evidence obtained from the present meta-analysis.10
Outcome assessment
The primary outcome was the prevalence of suspected or confirmed COVID-19 with a positive PCR test for SARS-CoV-2 in ADs. The numbers of patients with COVID-19 and confirmed cases in each of studies are shown in online supplemental table S1. To conduct subgroup analyses with each diagnosis, we classified ADs based on the digestive, musculoskeletal and integumentary systems. Diseases of the digestive system were categorised into IBD and autoimmune hepatic diseases (AHD). Rheumatic diseases (RD) included rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, vasculitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS), systemic sclerosis (SSc) and other autoimmune-mediated diseases (including Behcet’s syndrome, sarcoidosis and inflammatory myopathies). Given that several studies of RD focused only on patients with SLE, SjS or SSc, these studies were categorised into ‘SLE/SjS/SSc’. Diseases of the skin were categorised as ‘psoriasis/autoimmune skin diseases (AISD)’. Two studies included various ADs and were classified as ‘immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID)’.11 12
Supplemental material
Secondary outcomes included the following COVID-19 clinical outcomes: (1) hospitalisation, (2) intensive care unit (ICU) admission, (3) mechanical or non-invasive ventilation and (4) death. Subgroup analyses evaluating individual comorbidities13 and medication use prior to COVID-19 diagnosis were conducted. We divided medication use into the following three categories: (1) GCs, (2) conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs), (3) biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs (b/tsDMARDs). Budesonide, which is used as an ileal release form in IBD, was not included in the GCs when data were available. csDMARDs included hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, thiopurines, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, leflunomide, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil/mycophenolic acid and sulfasalazine. b/tsDMARDs included abatacept, belimumab, CD-20, interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-12/23, IL-23, IL-17, TNF, α4β7 integrin and Janus kinase inhibitors.3 We also divided b/tsDMARDs into monotherapy and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy if studies separately presented the data. If not, we considered b/tsDMARDs as utilised as a monotherapy.
Statistical analysis
We undertook a meta-analysis of the prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 among individuals with ADs from observational or case–control studies by using a random effects model. We evaluated the presence of heterogeneity across studies by using the I 2 statistic. An I 2 value of <25% indicates low heterogeneity, 25%–75% as moderate heterogeneity and >75% as considerable heterogeneity.14 Heterogeneity was evaluated by using Cochran’s Q-statistics with a significance level of p<0.10.15 Begg’s and Egger’s tests were performed to access publication bias and funnel plots were constructed to visualise possible asymmetry when three or more studies were available.16 17 A random effects meta-regression model was used to assess the contributions of each of potential risk factors and medication class to the prevalence and adverse clinical outcomes. If the number of available studies for each analysis was less than 10, we did not perform meta-regression analysis due to its low reliability.
Statistical analyses were performed using the Comprehensive Meta Analysis Software (V.3.0; Biostat, Englewood, NJ, USA). All statistical tests except for the Q-statistics used a two-sided p-value of 0.05 for significance.
Results
Study characteristics
We identified 2918 citations through the literature search, excluded 2773 titles and abstracts after initial screening and assessed 145 studies for eligibility. A final number 89 full-text articles met all eligibility criteria. For the analysis of COVID-19 prevalence, we included 62 observational studies with a total of 319 025 patients with ADs. For clinical outcomes, we included 65 studies with 2766 patients with ADs diagnosed with COVID-19. Among these studies, we identified 11 studies with case–controlled data which compared the prevalence or clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with ADs to those without ADs or the general population (figure 1). The characteristics and outcomes of the included studies are summarised in online supplemental table S1.
Prevalence of COVID-19 in autoimmune diseases
Meta-analysis of 62 observational studies including 319 025 patients with ADs from 15 countries showed that the prevalence of COVID-19 was 0.011 (95% CI: 0.005 to 0.025) (figure 2A). In the subgroup analyses, the prevalence of COVID-19 in AHD, IBD, psoriasis/AISD, RD and SLE/SjS/SSc were 0.036 (95% CI: 0.004 to 0.258), 0.003 (95% CI: 0.001 to 0.006), 0.011 (95% CI: 0.006 to 0.021), 0.009 (95% CI: 0.005 to 0.014), 0.034 (95% CI: 0.014 to 0.080), respectively, with IBD having the lowest prevalence (figure 2A). SLE/SjS/SSc showed a higher prevalence (0.034) when compared with the other disease groups, which is likely due to a higher proportion of GC use (60.3%) in the SLE/SjS/SSc subgroup (online supplemental table S1). Heterogeneity was considerable in overall (I 2=96.8%) and most subgroup analyses, which was primarily due to the difference in study sizes. The funnel plot was not asymmetric, indicating no publication bias, which was supported by Egger’s test (p=0.083) but not Begg’s test (p=0.002) (online supplemental figure S1). The subgroup analysis according to country showed that the prevalence range of COVID-19 was 0.002–0.012, with European countries having the highest prevalence (online supplemental figure S2).
Supplemental material
(A) Meta-analysis of observational studies to determine the prevalence of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases. (B) Meta-analysis of case–controlled studies to compare the prevalence of COVID-19 in autoimmune diseases with those without autoimmune diseases or general population.
Meta-analysis of seven case–controlled studies showed that the risk of COVID-19 in ADs was significantly higher than in control patients (OR: 2.19, 95% CI: 1.05 to 4.58, p=0.038). These studies only included individuals with psoriasis and RD, and both diseases demonstrated an elevated risk of COVID-19 as compared with controls (OR: 3.43, 95% CI: 1.68 to 7.01, p=0.001, OR: 1.60, 95% CI: 1.13 to 2.25, p=0.008, respectively) (figure 2B). There was low to considerable heterogeneity in overall (I 2=78.0%) and in each subgroup analysis (I 2=0% with psoriasis, and I 2=53.1% with RD). No publication bias was detected by Begg’s and Egger’s tests (Begg: p=1.00, Egger: p=0.25) (online supplemental figure S3).
Meta-regression analysis of the variables potentially associated with the risk of COVID-19 showed that studies with a higher proportion of GC use in patients with ADs had a higher prevalence of COVID-19 (regression coefficient: 0.020, 95% CI: 0.001 to 0.040, p=0.042). Meanwhile, age, proportion of males, hypertension, diabetes or therapies including csDMARDs and b/tsDMARDs did not contribute to the risk of COVID-19 (table 1).
Meta-regression of the variables potentially associated with the prevalence of COVID-19
Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in autoimmune diseases
Meta-analysis of 65 observational studies including 2766 patients with ADs diagnosed with COVID-19 showed that the hospitalisation rate due to COVID-19 was 0.35 (95% CI: 0.23 to 0.50) (figure 3A). Hospitalisation rates of AHD, IBD, IMID, psoriasis/AISD, RD and SLE/SjS/SSc were 0.52 (95% CI: 0.23 to 0.80), 0.29 (95% CI: 0.21 to 0.38), 0.24 (95% CI: 0.12 to 0.43), 0.26 (95% CI: 0.15 to 0.41), 0.54 (95% CI: 0.46 to 0.63) and 0.33 (95% CI: 0.20 to 0.49), respectively, with RD having the highest hospitalisation rate. Studies of RD included more elderly patients and patients with comorbidities (online supplemental table S1). Heterogeneity was considerable in overall (I 2=81.8%) and moderate to considerable in subgroup analyses (I 2=28.1%–79.9%) except for AHD (I 2=0%). Funnel plot demonstrated no asymmetry, therefore suggesting there was no small-study effects or publication bias, which was supported by Begg’s and Egger’s tests (online supplemental figure S4A).
(A) Meta-analysis of observational studies to assess the hospitalisation rate of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases. (B) Meta-analysis of observational studies to assess the mortality rate of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases.
The mortality due to COVID-19 in patients with ADs was 0.066 (95% CI: 0.036 to 0.12) (figure 3B). Mortality of AHD, IBD, IMID, psoriasis/AISD, RD and SLE/SjS/SSc were 0.094 (95% CI: 0.019 to 0.36), 0.045 (95% CI: 0.032 to 0.063), 0.017 (95% CI: 0.004 to 0.065), 0.097 (95% CI: 0.042 to 0.21), 0.113 (95% CI: 0.098 to 0.13) and 0.069 (95% CI: 0.032 to 0.14), respectively. Patients with RD had the highest mortality rate, which was consistent with the analysis of the hospitalisation rate. Heterogeneity was moderate in overall (I 2=26.6%) and absent in subgroup analyses (I 2=0%) except for IBD (I 2=49%). Begg’s (p=0.003), but not Egger’s (p=0.093), test was suggestive of publication bias, but the funnel plot was not asymmetric (online supplemental figure S4B). Overall rates of ICU admission and mechanical or non-invasive ventilation were 0.087 (95% CI: 0.045 to 0.16) (online supplemental figure S5A) and 0.11 (95% CI: 0.063 to 0.18) (online supplemental figure S5B), respectively.
Meta-analysis of six case–controlled studies showed no differences in hospitalisations (OR: 1.05, 95% CI: 0.78 to 1.42, p=0.73) (figure 4A), death (OR: 0.55, 95% CI: 0.081 to 3.68, p=0.53) (figure 4B), ICU admission (OR: 1.22, 95% CI: 0.42 to 3.60, p=0.72) (online supplemental figure S6A) or mechanical/non-invasive ventilation (OR: 1.03, 95% CI: 0.22 to 4.81, p=0.97) when compared with the control population (online supplemental figure S6B). Each disease subgroup did not show any remarkable differences in these clinical outcomes. All analyses showed low to moderate heterogeneity (I 2=0%–73.5%) and no publication bias (online supplemental figure S6C,D and S7).
(A) Meta-analysis of case–controlled studies to assess the hospitalisation rate of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases. (B) Meta-analysis of case–controlled studies to assess the mortality rate of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases.
Subgroup analyses according to comorbidities showed that patients with age ≥64 years old, male gender, hypertension, diabetes, BMI ≥30 and at least one comorbidity had higher rates of hospitalisation, ICU admission, ventilation and death due to COVID-19 when compared with those without these comorbidities (online supplemental table S2). Subgroup analyses according to medical therapies showed that patients treated with GCs, csDMARDs or b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy had a 2–3 times higher event rate of each clinical outcome when compared with those treated with b/tsDMARDs monotherapy (online supplemental table S3). Importantly, patients with anti-TNF monotherapy use tended to have a lower rate of hospitalisation and mortality when compared with those with non-TNF-targeted monotherapy (online supplemental table S3). Analysis of hospitalisation rates showed moderate heterogeneity, but most other analyses had low heterogeneity (online supplemental tables S2 and S3).
Meta-regression analysis showed that older age (regression coefficient: 0.070, 95% CI: 0.046 to 0.095, p<0.001), a higher proportion of patients with hypertension (regression coefficient: 0.017, 95% CI: 0.002 to 0.032, p=0.024), or at least one comorbidity (regression coefficient: 0.024, 95% CI: 0.007 to 0.040, p=0.004) in patients with ADs and COVID-19 had a higher risk of hospitalisation due to COVID-19. Older age (regression coefficient: 0.068, 95% CI: 0.048 to 0.089, p<0.001), a higher proportion of hypertension (regression coefficient: 0.034, 95% CI: 0.022 to 0.045, p<0.001) and diabetes (regression coefficient: 0.038, 95% CI: 0.012 to 0.064, p=0.004) were associated with a higher mortality rate due to COVID-19 (table 2). In terms of treatments, studies with a greater proportion of patients on csDMARDs or b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy showing a higher rate of hospitalisation or death and conversely, studies with a higher proportion of patients on b/tsDMARDs monotherapy, particularly anti-TNF monotherapy, had a lower rate of hospitalisation and mortality due to COVID-19. A higher proportion of GC use tended to be associated with a higher rate of hospitalisation and death, although this result was not statistically significant (table 2).
Meta-regression of the variables potentially associated with clinical outcomes of COVID-19
Grading the quality of evidence
Based on the GRADE approach, an overall quality of evidence for this analysis was moderate as the heterogeneity was considerable (online supplemental table S4).
Discussion
Our meta-analysis showed that although patients with ADs have a higher prevalence of COVID-19, their clinical outcomes were not considerably worse when compared with individuals without ADs. Meta-regression analysis demonstrated that prior GC use was associated with the increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection. We also found that the following factors associated with severe COVID-19 outcomes: (1) GC use, (2) older age, (3) comorbidities such as hypertension or diabetes, (4) csDMARDs and (5) b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy. However, b/tsDMARDs monotherapy, particularly anti-TNF therapy, was associated with reduced risk of hospitalisation and mortality due to COVID-19.
Our data showed that the prevalence of COVID-19 in ADs was 0.011 (95% CI: 0.005 to 0.025) and subgroup analysis revealed the prevalence in IBD was lower than that in RD or SLE/SjS/SSc. Previous studies have also reported differences in the prevalence of COVID-19 in patients with IBD (0.4%18) and RD (0.76%).19 Our meta-regression analysis demonstrated that GC use prior to COVID-19 significantly contributed to the disease prevalence. Indeed, the mean percentage of GC use in studies of IBD (12.6%) was lower than in RD (37.8%) and SLE/SjS/SSc (60.3%), suggesting that the differential infectious risk among diseases might be attributed to GC use prior to developing COVID-19. Recent studies showed that active disease and GC use were associated with higher risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection20 or severe COVID-1921 in patients with ADs. Another study reported on the beneficial effect of dexamethasone in reducing mortality among those hospitalised with COVID-19.22 Further investigations into the use of GCs in patients with ADs and the risk of COVID-19 in patients with active disease requiring GCs are needed.
In terms of the clinical outcomes, we found that the subgroup of RD had the highest rate of hospitalisation and mortality due to COVID-19. Our meta-regression analysis demonstrated that older age, comorbidities, csDMARDs and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy contributed to severe COVID-19 outcomes. Supporting this result, the mean age (58.3 years), proportion of individuals with underlying comorbidities (71.8%) and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy use (33.1%) was highest in the RD subgroup when compared with all other disease subgroups. Meanwhile, our data showed that b/tsDMARDs monotherapy, particularly anti-TNF therapy, might be protective against severe COVID-19. This finding was consistent with the C19-GRA registry which reported that the hospitalisation rate of RD patients treated with csDMARDs and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy was 55% and 36%, respectively, whereas those with b/tsDMARDs monotherapy had a lower hospitalisation rate (29%).3 A recent study which assessed associations between serum levels of cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF and COVID-19 outcomes demonstrated that an increased level of TNF can be a predictor of poor outcomes in patients under 70 years.23 These findings suggested that anti-TNF therapies might prevent severe COVID-19, however, further investigations are needed because anti-TNF drugs are associated with increased risk of serious infections in ADs.24 25
Limitations
Meta-analyses of observational studies regarding the prevalence of COVID-19 and hospitalisation rate had considerable heterogeneities. The cause of this heterogeneity could be potentially explained by the differences in study size, inclusion of different diseases and study location. Thus, we undertook subgroup analyses and performed meta-regression to assess the effect of each potential risk factor on the individual outcomes. Subgroup analyses regarding the hospitalisation outcome revealed low-moderate heterogeneities, which suggested that the difference among subgroups contributed to the initial heterogeneity. Second, although we assessed the effect of b/tsDMARDs monotherapy and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy on the outcomes separately, not all studies presented data in these two groups. In a situation where csDMARDs were stopped for fear of COVID-19 in patients on combination therapies, washout periods of csDMARDs could not be considered. Third, the sensitivity of RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 from nasopharyngeal swab is roughly 70%.26 27 Meanwhile, although there was no guideline regarding COVID-19 testing in patients starting immunosuppressants,28 patients with ADs might have been tested earlier and more frequently compared with the general population due to their concern of infectious risk of SARS-CoV-2. Hence, these issues might affect the result of the prevalence data in our meta-analysis.
Conclusion
This study is the first comprehensive meta-analysis which determined the prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in ADs. Our study suggests that GC use increases the risk of SARS-CoV2 infection and might contribute to the higher prevalence of COVID-19 in ADs. Although GCs, csDMARDs and b/tsDMARDs–csDMARDs combination therapy contributed to disease severity in COVID-19, b/tsDMARDs monotherapy, especially anti-TNF monotherapy, was associated with reduced risk of severe disease. Our meta-analysis provides evidence that b/tsDMARDs monotherapy can be safely used during the pandemic.
References
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Data
This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
Lay summary
Disclaimer : This is a summary of a scientific article written by a medical professional (“the Original Article”). The Summary is written to assist non medically trained readers to understand general points of the Original Article. It is supplied “as is” without any warranty. You should note that the Original Article (and Summary) may not be fully relevant nor accurate as medical science is constantly changing and errors can occur. It is therefore very important that readers not rely on the content in the Summary and consult their medical professionals for all aspects of their health care and only rely on the Summary if directed to do so by their medical professional. Please view our full Website Terms and Conditions.
Copyright © 2021 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd & European League Against Rheumatism. Medical professionals may print copies for their and their patients and students non commercial use. Other individuals may print a single copy for their personal, non commercial use. For other uses please contact our Rights and Licensing Team.
Footnotes
Handling editor Josef S Smolen
Contributors Literature search: SA, SH and AS. Figures creation: SA. Study design: SA and AS. Data collection: SA and AS. Data analysis: SA. Data interpretation: SA and AS. Drafting of manuscript: SA, DM and AS. Full responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, from inception to published article: AS.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information. All data relevant to the study are included in the article and uploaded as supplementary information.
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.