Article Text
Abstract
Background Osteoarthritis (OA) in the hand often associates with considerable disability and a reduced quality of life that is comparable to the effects of rheumatoid arthritis. GCSB-5 is a mixture of six purified oriental herb extracts, which have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and chondroprotective effects.
Objectives To investigate the efficacy and safety of GCSB-5 for treating hand OA, a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter trial was conducted.
Methods Patients with hand OA who had baseline visual analog scale joint pain scores exceeding >30/100 mm were included. After randomization, patients were allocated to receive oral GCSB-5 600 mg or placebo twice daily for 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was a change in the Australian/Canadian Osteoarthritis Hand Index (AUSCAN) pain score at 4 weeks relative to baseline. Secondary endpoints included AUSCAN pain at 8, 12, and 16 weeks, AUSCAN stiffness and function, patient global assessment score, and the frequency of patients with an Outcome Measures in Rheumatology-Osteoarthritis Research Society (OMERACT-OARSI) response at all time points. The study was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov, protocol number NCT01910116.
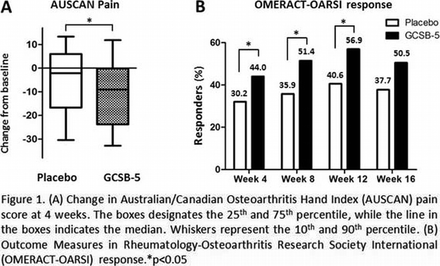
Results The allocated treatment was received by 109 and 106 patients in the GCSB-5 and placebo groups, respectively. At 4 weeks, improvement of the AUSCAN pain score relative to baseline was significantly better in the GCSB-5 group as compared to the placebo group (median -9.0 [interquartile range (IQR) -23.8, -0.2] vs. -2.2 [-16.7, 6.0]; p=0.014). The improvement remained better at 8 (-13.4 [-26.8, 0] vs. -2.2 [-17.5, 5.0]; p=0.011), 12 (-14.60 [-30.8, 0] vs. -8.00 [-25.3, 7.8]; p=0.054), and 16 (-15.60 [-28.2, 0] vs. -4.40 [-25.1, 7.3]; p=0.014) weeks in the GCSB-5 group. The GCSB-5 group also had a significantly higher OMERACT-OARSI response rate than the placebo group at 4 (44.0% vs. 30.2%; p=0.036), 8 (51.4% vs. 35.9%; p=0.022), 12 (56.9% vs. 40.6%; p=0.017), and 16 (50.5% vs. 37.7%; p=0.060) weeks. There were no serious adverse events and the two groups exhibited comparable safety profiles.
Conclusions GCSB-5 improved the symptoms of hand OA and had a tolerable safety profile.
Disclosure of Interest J. K. Park: None declared, K. Shin: None declared, E.-H. Kang: None declared, Y.-J. Ha: None declared, K. H. Lee: None declared, E. Y. Lee: None declared, Y. J. Lee: None declared, Y. W. Song: None declared, E. B. Lee Consultant for: Pfizer