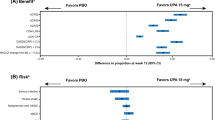
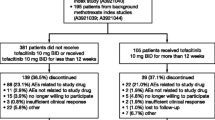
Abstract
The management of rheumatoid arthritis has seen a dramatic improvement with the introduction of a range of biological disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in recent years. Nonetheless, a proportion of patients remain resistant or intolerant to multiple conventional and biological DMARDs, so innovative strategies are needed to offer patients new therapeutic options. Tofacitinib is the first of a new class of orally active DMARDs, with immunomodulating effects through inhibition of intracellular Janus kinase (JAK) pathways. It has been recently licensed for treatment of adults with moderate to severe RA in the US, Japan, and Russia. In this review the authors evaluate the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in RA, focusing predominantly on the phase 3 study data.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sokka T, Krishnan E, Hakkinen A, Hannonen P. Functional disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients compared with a community population in Finland. Arthritis Rheum. [Comparative Study Research Support, Non-US Gov’t]. 2003;48(1):59–63.
Combe B. Early rheumatoid arthritis: strategies for prevention and management. Best practice and research Clinical rheumatology. [Review] 2007;21(1):27–42.
Canete JD, Pablos JL. Biologic Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013.
Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, van Zeben D, Kerstens PJ, Hazes JM, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the BeSt study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(11):3381–90.
Wolfe F, Michaud K. Resistance of rheumatoid arthritis patients to changing therapy: discordance between disease activity and patients’ treatment choices. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(7):2135–42.
Ghoreschi K, Jesson MI, Li X, Lee JL, Ghosh S, Alsup JW, et al. Modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by tofacitinib (CP-690,550). J Immunol. 2011;186(7):4234–43.
Pfizer. US Full Prescribing Information. http://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=959. 2012 [25 April 2013].
Ghoreschi K, Laurence A, O’Shea JJ. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol Rev. 2009;228(1):273–87.
Riese RJ, Krishnaswami S, Kremer J. Inhibition of JAK kinases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: scientific rationale and clinical outcomes. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010;24(4):513–26.
Levy DE, Darnell JE Jr. Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(9):651–62.
Meyer DM, Jesson MI, Li X, Elrick MM, Funckes-Shippy CL, Warner JD, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity and neutrophil reductions mediated by the JAK1/JAK3 inhibitor, CP-690,550, in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Inflamm. 2010;7:41.
Kremer JM, Bloom BJ, Breedveld FC, Coombs JH, Fletcher MP, Gruben D, et al. The safety and efficacy of a JAK inhibitor in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa trial of three dosage levels of CP-690,550 versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(7):1895–905.
Fleischmann R, Cutolo M, Genovese MC, Lee EB, Kanik KS, Sadis S, et al. Phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) or adalimumab monotherapy versus placebo in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(3):617–29.
Kremer JM, Cohen S, Wilkinson BE, Connell CA, French JL, Gomez-Reino J, et al. A phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) versus placebo in combination with background methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate alone. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(4):970–81.
Tanaka Y, Suzuki M, Nakamura H, Toyoizumi S, Zwillich SH. Tofacitinib Study I. Phase II study of tofacitinib (CP-690,550) combined with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63(8):1150–8.
Burmester GR, Blanco R, Charles-Schoeman C, Wollenhaupt J, Zerbini C, Benda B, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550) in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381(9865):451–60.
van der Heijde D, Tanaka Y, Fleischmann R, Keystone E, Kremer J, Zerbini C, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate: twelve-month data from a twenty-four–month phase III randomized radiographic study. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(3):559–70.
van Vollenhoven RF, Fleischmann R, Cohen S, Lee EB, Garcia Meijide JA, Wagner S, et al. Tofacitinib or adalimumab versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(6):508–19.
Fleischmann R, Kremer J, Cush J, Schulze-Koops H, Connell CA, Bradley JD, et al. Placebo-controlled trial of tofacitinib monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(6):495–507.
Lee EB, Fleischmann RM, Hall S, van Vollenhoven RF, Bradley J, Gruben D. Radiographic, clinical and functional comparison of tofacitinib monotherapy versus methotrexate in methotrexate-naive patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64 (Suppl 10).
Kremer J, Li ZG, Hall JR, Fleischmann R, Genovese MC, Martin-Mola E. Tofacitinib (CP = 690,550), an oral JAK inhibitor, in combination with traditional DMARDs, Phase 3 study in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to DMARDs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 2011;70 (Suppl3): 170.
van der Heijde D. How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. J Rheumatol. [Corrected and Republished Article]. 2000;27(1):261–3.
Pfizer. Advisory Committee Meeting: Tofacitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/ArthritisAdvisoryCommittee/UCM302960.pdf. 2013 [25 April 2013].
Winthrop KL, Park S-H, Gul A, Cardiel M, Gomez-Reino J, Ponce de Leon D, et al. Tuberculosis and tofacitinib therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10 suppl):S547.
Cohen S, Radominski SC, Asavatanabodee P, Wood SP, Soma K. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550), An oral Janus kinase inhibitor: analysis of infections and all-cause mortality across phase 3 and long-term extension studies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63 (Suppl 10).
Mariette X, Curtis JR, Lee EB, Riese R, Kaplan I, Chew R, et al. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor: analysis of malignancies across the rheumatoid arthritis clinical programme. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;2012;71(Suppl3):199.
Lee EB, Curtis JR, Riese R, Connell CA, Chew R, Boy M, et al. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor: analysis of gastrointestinal adverse events across the rheumatoid arthritis clinical programme. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(Suppl 3):202.
Schiff MH, Kremer JM, Jahreis A, Vernon E, Isaacs JD, van Vollenhoven RF. Integrated safety in tocilizumab clinical trials. Arthritis Res Ther. [Clinical Trial, Phase III Comparative Study Randomized Controlled Trial Research Support, Non-US Gov’t]. 2011;13(5):R141.
Acknowledgments
Prior to peer review Pfizer was offered the opportunity to review this paper for scientific accuracy. No writing assistance, other editorial involvement, or financial support was provided by the manufacturer in the production of this manuscript. This article does not necessarily reflect the opinions, policies, or recommendations of Pfizer or any of its employees. Dr. Rakieh is the guarantor for this article, and takes responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole.
Conflict of interest
Phil G. Conaghan has attended speaker meetings or advisory boards for BMS, Janssen, Pfizer and Roche. Chadi Rakieh declares no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakieh, C., Conaghan, P.G. Tofacitinib for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adv Ther 30, 713–726 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-013-0047-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-013-0047-y