Abstract
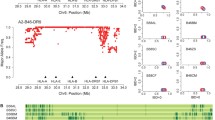
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the human genome are thought to be organised into blocks of high internal linkage disequilibrium (LD), separated by intermittent recombination hotspots. Since understanding haplotype structure is critical for an accurate assessment of inter-individual genetic differences, we investigated up to 968 SNPs from a 10-Mb region on chromosome 6p21, including the human major histocompatibility complex (MHC), in five different population samples (45–550 individuals). Regions of well-defined block structure were found to coexist alongside large areas lacking any clear structure; occasional long-range LD was observed in all five samples. The four white populations analysed were remarkably similar in terms of the extend and spatial distribution of local LD. In US African Americans, the distribution of LD was similar to that in the white populations but the observed haplotype diversity was higher. The existence of large regions without any clear block structure renders the systematic and thorough construction of SNP haplotype maps a crucial prerequisite for disease-association studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad T, Neville M, Marshall SE, Armuzzi A, Mulcahy-Hawes K, Crawshaw J, Sato H, Ling KL, Barnardo M, Goldthorpe S, et al (2003) Haplotype-specific linkage disequilibrium patterns define the genetic topography of the human MHC. Hum Mol Genet 12:647–656
Allcock RJ, Christiansen FT, Price P (1999) The central MHC gene IKBL carries a structural polymorphism that is associated with HLA-A3,B7,DR15. Immunogenetics 49:660–665
Barbujani G, Bertorelle G (2001) Genetics and the population history of Europe. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:22–25
Becker KG, Simon RM, Bailey-Wilson JE, Freidlin B, Biddison WE, McFarland HF, Trent JM (1998) Clustering of non-major histocompatibility complex susceptibility candidate loci in human autoimmune diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9979–9984
Cereb N, Hughes AL, Yang SY (1997) Locus-specific conservation of the HLA class I introns by intra-locus homogenization. Immunogenetics 47:30–36
Cullen M, Perfetto SP, Klitz W, Nelson G, Carrington M (2002) High-resolution patterns of meiotic recombination across the human major histocompatibility complex. Am J Hum Genet 71:759–776
D’Alfonso S, Bolognesi E, Mazzola G, Dall’Omo A, Richiardi PM (1999) Historical recombinant sites in extended HLA haplotypes. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 13:8–13
Daly MJ, Rioux JD, Schaffner SF, Hudson TJ, Lander ES (2001) High-resolution haplotype structure in the human genome. Nat Genet 29:229–232
Dawson E, Abecasis GR, Bumpstead S, Chen Y, Hunt S, Beare DM, Pabial J, Dibling T, Tinsley E, Kirby S, et al (2002) A first-generation linkage disequilibrium map of human chromosome 22. Nature 418:544–548
De La Vega FM, Dailey D, Ziegle J, Williams J, Madden D, Gilbert DA (2002) New generation pharmacogenomic tools: a SNP linkage disequilibrium map, validated SNP assay resource, and high-throughput instrumentation system for large-scale genetic studies. Biotechniques Suppl:48–54
De La Vega FM, Su X, Avi-Itzhak HI, Halldorson BV, Gordon D, Collins A, Lippert R, Schwartz R, Scafe CR, Wang Y, et al (2003) Patterns of linkage disequilibrium across human chromosomes 6, 21, and 22 in African-American and Caucasian populations. Nat Genet (in press)
Frisse L, Hudson RR, Bartoszewicz A, Wall JD, Donfack J, Di Rienzo A (2001) Gene conversion and different population histories may explain the contrast between polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium levels. Am J Hum Genet 69:831–843
Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, Blumenstiel B, Higgins J, DeFelice M, Lochner A, Faggart M, et al (2002) The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296:2225–2229
Gaudieri S, Leelayuwat C, Tay GK, Townend DC, Dawkins RL (1997) The major histocompatability complex (MHC) contains conserved polymorphic genomic sequences that are shuffled by recombination to form ethnic-specific haplotypes. J Mol Evol 45:17–23
Goldstein DB (2001) Islands of linkage disequilibrium. Nat Genet 29:109–111
Guillon H, Massy B de (2002) An initiation site for meiotic crossing-over and gene conversion in the mouse. Nat Genet 32:296–299
Hampe J, Wollstein A, Lu T, Frevel HJ, Will M, Manaster C, Schreiber S (2001) An integrated system for high throughput TaqMan based SNP genotyping. Bioinformatics 17:654–655
Jeffreys AJ, Neumann R (2002) Reciprocal crossover asymmetry and meiotic drive in a human recombination hot spot. Nat Genet 31:267–271
Jeffreys AJ, Murray J, Neumann R (1998) High-resolution mapping of crossovers in human sperm defines a minisatellite-associated recombination hotspot. Mol Cell 2:267–273
Jeffreys AJ, Kauppi L, Neumann R (2001) Intensely punctate meiotic recombination in the class II region of the major histocompatibility complex. Nat Genet 29:217–222
Johnson GC, Esposito L, Barratt BJ, Smith AN, Heward J, Di Genova G, Ueda H, Cordell HJ, Eaves IA, Dudbridge F, et al (2001) Haplotype tagging for the identification of common disease genes. Nat Genet 29:233–237
Kauppi L, Sajantila A, Jeffreys AJ (2003) Recombination hotspots rather than population history dominate linkage disequilibrium in the MHC class II region. Hum Mol Genet 12:33–40
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, New York
Lercher MJ, Hurst LD (2002) Human SNP variability and mutation rate are higher in regions of high recombination. Trends Genet 18:337–340
Lewontin RC (1988) On measures of gametic disequilibrium. Genetics 120:849–852
Lonjou C, Zhang W, Collins A, Tapper WJ, Elahi E, Maniatis N, Morton NE (2003) Linkage disequilibrium in human populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 29:29
Maniatis N, Collins A, Xu CF, McCarthy LC, Hewett DR, Tapper W, Ennis S, Ke X, Morton NE (2002) The first linkage disequilibrium (LD) maps: delineation of hot and cold blocks by diplotype analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2228–2233
May CA, Shone AC, Kalaydjieva L, Sajantila A, Jeffreys AJ (2002) Crossover clustering and rapid decay of linkage disequilibrium in the Xp/Yp pseudoautosomal gene SHOX. Nat Genet 31:272–275
Meyer D, Thomson G (2001) How selection shapes variation of the human major histocompatibility complex: a review. Ann Hum Genet 65:1–26
Morton NE, Zhang W, Taillon-Miller P, Ennis S, Kwok PY, Collins A (2001) The optimal measure of allelic association. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5217–5221
Phillips MS, Lawrence R, Sachidanandam R, Morris AP, Balding DJ, Donaldson MA, Studebaker JF, Ankener WM, Alfisi SV, Kuo FS, et al (2003) Chromosome-wide distribution of haplotype blocks and the role of recombination hot spots. Nat Genet 33:382–387
Reich DE, Cargill M, Bolk S, Ireland J, Sabeti PC, Richter DJ, Lavery T, Kouyoumjian R, Farhadian SF, Ward R, et al (2001) Linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nature 411:199–204
Reich DE, Schaffner SF, Daly MJ, McVean G, Mullikin JC, Higgins JM, Richter DJ, Lander ES, Altshuler D (2002) Human genome sequence variation and the influence of gene history, mutation and recombination. Nat Genet 32:135–142
Sanchez-Mazas A, Djoulah S, Busson M, Le Monnier de Gouville I, Poirier JC, Dehay C, Charron D, Excoffier L, Schneider S, Langaney A, et al (2000) A linkage disequilibrium map of the MHC region based on the analysis of 14 loci haplotypes in 50 French families. Eur J Hum Genet 8:33–41
Schneider S, Roessli D, Excoffier L (2000) Arlequin: a software for population genetics data analysis, ver 2.000. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, Department of Anthropology, University of Geneva
Simoni L, Calafell F, Pettener D, Bertranpetit J, Barbujani G (2000) Geographic patterns of mtDNA diversity in Europe. Am J Hum Genet 66:262–278
Stephens JC, Reich DE, Goldstein DB, Shin HD, Smith MW, Carrington M, Winkler C, Huttley GA, Allikmets R, Schriml L, et al (1998) Dating the origin of the CCR5-Delta32 AIDS-resistance allele by the coalescence of haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 62:1507–1515
Tapper WJ, Ke X, Morton NE, Collins A (2002) Recombination, interference and sequence: comparison of chromosomes 21 and 22. Ann Hum Genet 66:75–86
Teare MD, Dunning AM, Durocher F, Rennart G, Easton DF (2002) Sampling distribution of summary linkage disequilibrium measures. Ann Hum Genet 66:223–233
Walsh EC, Mather KA, Schaffner SF, Farwell L, Daly MJ, Patterson N, Cullen M, Carrington M, Bugawan TL, Erlich H, Campbell J, Barrett J, Miller K, Thomson G, Lander ES, Rioux JD (2003) An integrated haplotype map of the human major histocompatibility complex. Am J Hum Genet 73:580–590
Wang WY, Todd JA (2003) The usefulness of different density SNP maps for disease association studies of common variants. Hum Mol Genet 12:3145–3149
Zavattari P, Deidda E, Whalen M, Lampis R, Mulargia A, Loddo M, Eaves I, Mastio G, Todd JA, Cucca F (2000) Major factors influencing linkage disequilibrium by analysis of different chromosome regions in distinct populations: demography, chromosome recombination frequency and selection. Hum Mol Genet 9:2947–2957
Zhang K, Akey JM, Wang N, Xiong M, Chakraborty R, Jin L (2003) Randomly distributed crossovers may generate block-like patterns of linkage disequilibrium: an act of genetic drift. Hum Genet 113:51–59
Acknowledgements
The authors thank physicians and technicians at the Kiel blood bank (headed by J. Neppert) for the recruitment of healthy German individuals, and M. Vatn, Oslo, Norway, and C. Mathew, London, UK, for providing local population samples. We acknowledge the expert technical help of T. Wesse and the entire technical staff of the Mucosal Research Laboratory, Kiel. Thanks are also due to J. Ziegle, L. Wogan and the production genotyping team of Services Development and Delivery of Applied Biosystems, and to A. Collins, Southampton, UK, for providing the LDMAP software. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (FOR 423), the European Commission (QLG2-CT-2001-02161), and the German Ministry for Education and Research (Competence Network “Inflammatory Bowel Disease”, German Human Genome Project, National Genome Research Network).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic database information: URLs for the data in this article are as follows:
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stenzel, A., Lu, T., Koch, W.A. et al. Patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the MHC region on human chromosome 6p. Hum Genet 114, 377–385 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-003-1075-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-003-1075-5