Abstract
Purpose
There are no biological markers available to predict outcome in melanoma patients treated with adjuvant interferon-alpha (IFN-α). The clinical activity of IFN-α is thought to be mediated not only by anti-proliferative effects, but also by induction and modulation of secondary cytokines. We examined serum cytokine levels in IFN-α-treated patients to find potential biological markers for response or toxicity.
Patients and methods
In a prospective randomized trial, 66 stages II and III melanoma patients underwent an induction treatment of 10 MU IFN α2b s.c. 5×/week, followed by either 5 MU or 10 MU IFN α2b s.c. 3×/week for a total of 2 years. Serial measurements of serum IL-1β, IL-2, sIL-2R, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α and β-2 microglobulin (B2M) were taken. Two factorial analysis of repeated measurements (ANOVA) as well as univariate and multivariate analyses was used to identify prognostic factors for relapse and toxicity.
Results
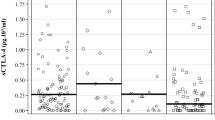
TNF-α levels correlated with toxicity. In patients with relapse, significantly lower levels of TNF-α were detected at baseline and throughout therapy compared with patients without relapse. B2M and sIL-2R showed a significant increase throughout the therapy phase. At baseline, the combination of TNF-α, B2M and sIL-2R revealed a positive predictive value for relapse of 82.9% in the multivariate analyses.
Conclusion
Low TNF-α levels are negatively associated with relapse-free survival. Conversely, high TNF-α levels are correlated with toxicity but seem to be beneficial to patients with regard to relapse-free survival. B2M and sIL-2R are biological markers of adjuvant IFN-α2b treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antony PA, Restifo NP (2005) CD4(+)CD25(+) T regulatory cells, immunotherapy of cancer, and interleukin-2. J Immunother 28:120–128
Bongartz T, Sutton AJ, Sweeting MJ, Buchan I, Matteson EL, Montori V (2006) Anti-TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies: Systematic review and meta-analysis of rare harmful effects in randomized controlled trials. JAMA 295:2275–2285
Boyano MD, Garcia-Vazquez MD, Lopez-Michelena T, Gardeazabal J, Bilbao J, Canavate ML, Galdeano AG, Izu R, Diaz-Ramon L, Raton JA, Diaz-Perez JL (2000) Soluble interleukin-2 receptor, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and interleukin-10 serum levels in patients with melanoma. Br J Cancer 83:847–852
Brunner E, Langer S (1999) Nichtparametrische Analyses longitudinaler Daten. Oldenburg Verlag, Munic
Calzascia T, Pellegrini M, Hall H, Sabbagh L, Ono N, Elford AR, Mak TW, Ohashi PS (2007) TNF-alpha is critical for antitumor but not antiviral T cell immunity in mice. J Clin Invest 117:3833–3845
Cao MG, Auge JM, Molina R, Marti R, Carrera C, Castel T, Vilella R, Conill C, Sanchez M, Malvehy J, Puig S (2007) Melanoma inhibiting activity protein (MIA), beta-2 microglobulin and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in metastatic melanoma. Anticancer Res 27:595–599
Edwards-Smith CJ, Jonsson JR, Purdie DM, Bansal A, Shorthouse C, Powell EE (1999) Interleukin-10 promoter polymorphism predicts initial response of chronic hepatitis C to interferon alfa. Hepatology 30:526–530
Eggermont AMM, Suciu S, MacKie R, Ruka W, Testori A, Kruit W, Punt CJA, Delauney M, Sales F, Groenewegen G, Ruiter DJ, Jagiello I, Stoitchkov K, Keilholz U, Lienard D (2005) Post-surgery adjuvant therapy with intermediate doses of interferon alfa 2b versus observation in patients with stage IIb/III melanoma (EORTC 18952): randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366:1189–1196
Eskdale J, Gallagher G (1995) A polymorphic dinucleotide repeat in the human Il-10 promoter. Immunogenetics 42:444–445
Feldmann M (2002) Development of anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 2:364–371
Gogas H, Ioannovich J, Dafni U, Stavropoulou-Giokas C, Frangia K, Tsoutsos D, Panagiotou P, Polyzos A, Papadopoulos O, Stratigos A, Markopoulos C, Bafaloukos D, Pectasides D, Fountzilas G, Kirkwood JM (2006) Prognostic significance of autoimmunity during treatment of melanoma with interferon. N Engl J Med 354:709–718
Grob JJ, Dreno B, de la Salmonière P, Delaunay M, Cupissol D, Guillot B, Souteyrand P, Sassolas B, Cesarini JP, Lionnet S, Lok C, Chastang C, Bonerandi JJ (1998) Randomised trial of interferon alpha-2a as adjuvant therapy in resected primary melanoma thicker than 1.5 mm without clinically detectable node metastases. French Cooperative Group on Melanoma. Lancet 351:1905–1910
Huang S, Xie K, Bucana CD, Ullrich SE, Bar-Eli M (1996) Interleukin 10 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of human melanoma cells: potential inhibition of angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 2:1969–1979
Kerbel RS (1992) Expression of multi-cytokine resistance and multi-growth factor independence in advanced stage metastatic cancer. Malignant melanoma as a paradig. Am J Pathol 141:519–524
Kirkwood JM, Strawderman MH, Ernstoff MS, Smith TJ, Borden EC, Blum RH (1996) Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol 14:7–17
Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sondak VK, Richards J, Flaherty LE, Ernstoff MS, Smith TJ, Rao U, Steele M, Blum RH (2000) High- and low-dose interferon alfa-2b in high-risk melanoma: first analysis of intergroup trial E1690/S9111/C9190. J Clin Oncol 18:2444–2458
Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sosman JA, Sondak VK, Agarwala SS, Ernstoff MS, Rao U (2001) High-dose interferon alfa-2b significantly prolongs relapse-free and overall survival compared with the GM2-KLH/QS-21 vaccine in patients with resected stage IIB-III melanoma: results of intergroup trial E1694/S9512/C509801. J Clin Oncol 19:2370–2380
Lapinski TW, Kot A, Prokopowicz D (2002) Concentration of b2-microglobulin and percentage of CD4 lymphocytes in peripheral blood in patients with chronic HCV infection during IFN-a therapy. Med Sci Monit 8:CR538–CR542
Levesque N, Mitchinson K, Lawrie D, Fedorak L, MacDonald D, Normand C, Pouliot JF (2008) Health management program: factors influencing completion of therapy with high-dose interferon alfa-2b for high-risk melanoma. Curr Oncol 15:36–41
Liu D, O’Day SJ, Yang D, Boasberg P, Milford R, Kristedja T, Groshen S, Weber JS (2004) Immune gene polymorphisms predict overall survival for stage IV melanoma patients treated with biochemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 22:722S
Martinez-Escribano JA, Moya-Quiles MR, Muro M, Montes-Ares O, Hernandez-Caselles T, Frias JF, Alvarez-Lopez MR (2002) Interleukin-10, interleukin-6 and interferon-gamma gene polymorphisms in melanoma patients. Melanoma Res 12:465–469
Moore KW, O’Garra A, de Waal MR, Vieira P, Mosmann TR (1993) Interleukin-10. Annu Rev Immunol 11:165–190
Ottaiano A, Leonardi E, Simeone E, Ascierto PA, Scala S, Calernma R, Bryce J, Caraco C, Satriano RA, Gianfranco N, Franco R, Botti G, Castello G (2006) Soluble interleukin-2 receptor in stage I-III melanoma. Cytokine 33:150–155
Pestka S, Krause CD, Walter MR (2004) Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol Rev 202:8–32
Sato T, McCue P, Masuoka K, Salwen S, Lattime EC, Mastrangelo MJ, Berd D (1996) Interleukin 10 production by human melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2:1383–1390
Scagnolari C, Bellomi F, Trombetti S, Casato M, Carlesimo M, Bagnato F, Lavolpe V, Bruno R, Millefiorini E, Antonelli L, Girardi E, Turriziani O, Antonelli G (2007) Expression of biomarkers of interferon type I in patients suffering from chronic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 147:270–276
Starkel P (2008) Genetic factors predicting response to interferon treatment for viral hepatitis C. Gut 57:440–442
Valencia X, Stephens G, Goldbach-Mansky R, Wilson M, Shevach EM, Lipsky PE (2006) TNF downmodulates the function of human CD4(+)CD25(hi) T-regulatory cells. Blood 108:253–261
Wheatley K, Ives N, Hancock B, Gore M, Eggermont A, Suciu S (2003) Does adjuvant interferon-alpha for high-risk melanoma provide a worthwhile benefit? A meta-analysis of the randomised trials. Cancer Treat Rev 29:241–252
Yurkovetsky ZR, Kirkwood JM, Edington HD, Marrangoni AM, Velikokhatnaya L, Winans MT, Gorelik E, Lokshin AE (2007) Multiplex analysis of serum cytokines in melanoma patients treated with interferon-alpha 2b. Clin Cancer Res 13:2422–2428
Acknowledgments
This trial was supported by a grant from Essex Pharma GmbH, Munich, Germany. We thank Ulrich Keilholz, M.D., for critically reading the manuscript and for constructive comments.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofmann, M.A., Kiecker, F., Küchler, I. et al. Serum TNF-α, B2M and sIL-2R levels are biological correlates of outcome in adjuvant IFN-α2b treatment of patients with melanoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137, 455–462 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0900-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0900-1