Abstract
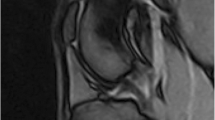
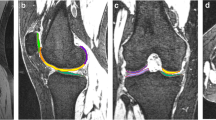
The objective of this study was to assess the normal range of cartilage volumes in the knee joints of healthy adults, the ratio between the patellar, femoral, and tibial cartilages, and the correlation of the volumes with age, body weight, height, body mass index (obesity), patellar bone size, and the diameter of the tibial head. We examined the knee joints of nine healthy volunteers and eleven normal post-mortem specimens with an age range of 24 to 82 years. The cartilage volumes of the patella, femur, medial tibia and the lateral tibia were quantified, using a fat-suppressed FLASH-3D sequence (resolution 2×0.31×0.31 mm3) and digital postprocessing, involving three-dimensional reconstruction. The mean total volume of the knee joint cartilage was 23,245 mm3, the relative standard deviation (CV%) 19%, and the range 16,341 to 33,988 mm3. In the patella, femur and tibia, the CV% amounted to between 22 and 25%. These joint surfaces occupied a relatively variable proportion of the total knee joint volume, the percentage of the patella being 11 to 22%, that of the femur 54 to 69%, that of the medial tibia 7 to 12%, and that of lateral tibia 11 to 16%. The volumes of the lateral tibia were systematically higher than those of the medial tibia (P<0.001). There was no significant correlation of the knee joint cartilage volume with age (r=+0.05), body weight (r=+0.38), height (r=+0.39) or body mass index (r=+0.29), but a relatively high correlation with the diameter of the tibial head (r=+0.78, P<0.001). After normalising the volumes to this diameter, the CV% of the total knee joint cartilge volume was reduced to 13%, its variation being 12 to 21% in the patella, femur and tibia. MRI is available for measuring cartilage volume during growth, functional adaptation, and tissue loss in degenerative joint disease. The study shows that a wide variation of cartilage volumes exists in the knee joints of normal adults. To reduce the variability between individuals, the cartilage volumes may be normalised to the head of the tibial diameter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 4 December 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eckstein, F., Winzheimer, M., Westhoff, J. et al. Quantitative relationships of normal cartilage volumes of the human knee joint – assessment by magnetic resonance imaging. Anat Embryol 197, 383–390 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004290050149
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004290050149