Summary
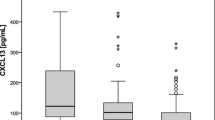
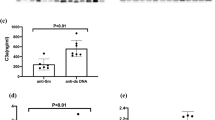
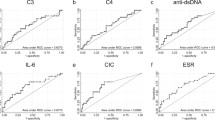
In order to investigate, if complement levels can be used as an indicator of clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), levels of C3, C4, CH50, and C3d were measured in 79 patients, 41 with inactive, 31 with moderately active and 7 with severely active disease. Our study shows that C3d, and particularly the C3d/C3 ratio, provide sensitive markers for disease activity in SLE. Since C3d is a direct measurement of complement turnover, it reflects complement activation better than C3, C4 and CH50.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourke, B.E., Moss, I.K., Maini, R.N. Measurement of the complement C3 breakdown product C3d by rocket immunoelectropheresis. J Immunol Methods 1982, 48, 97.
Brandslund, I., Sierstedt, H.C., Svehag, S.-E., Teisner, B. Double-decker-rocket immunoelectrophoresis for direct quantification of complement C3 split products with C3d specificities in plasma. J Immunol Methods 1981, 44, 63.
Charlesworth, J.A., Williams, D.G., Sherington, E., Lachmann, P.J., Peters, D.K. Metabolic studies of the third component of complement and the glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein in patients with hypocomplementemia. J Clin Invest 1974, 53, 1578–1587.
Clough, J.D., Chang, R.K. Effectiveness of testing for anti-DNA and the complement components iC3b, Bb, and C4 in the assessment of activity of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Lab Anal 1990, 4, 268–273.
Gewurz, H., Suyehira, L.A. Complement and immune complexes. In: Manual of Clinical Immunology, 2nd ed., Ed.: Roese, N., Friedmann, H., Washington, Am Soc Microbiol, 1980.
Hartung, K., Fontana, A., Klar, M., Krippner, H., Jörgens, K., Lang, B., Peter, H.H., Pichler, W.J., Schendel, D., Robin-Winn, M., Deicher, H. Association of class I, II, and III MHC gene products with systemic lupus erythematosus. Results of a Central European Multicenter Study. Rheumatol Int 1989, 9, 13–18.
Hopkins, P., Belmont, H.M., Buyon, J., Phillips, M., Weissmann, G., Abramson, S.B. Increased levels of plasma anaphylatoxins in systemic lupus erythematosus predict flares of the disease and may elicit vascular injury in lupus cerebritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988, 31, 632.
Inman, R.D., Fong, J.K.K., Pussell, B.A., Ryan, P.J., Hughes, G.R.V. The C1q binding assay in systemic lupus erythematosus: discordance with disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 1980, 23, 1282–1286.
Isenberg, D.A., Colaco, C.B., Dudeney, C., Todd-Pokropek, A., Snaith, M.L. The relationship of anti-DNA antibody idiotypes and anti-cardiolipin antibodies to disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1986, 65, 46–55.
Isenberg, D.A., Shoenfeld, Y., Schwartz, R.S. Multiple serological reactions and their relationship to clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1984, 27, 132–138.
Kerr, L.D., Adelsberg, B.R., Schulman, P., Spiera, H. Faktor B activation products in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. A marker of severe disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 1989, 32, 1406–1413.
Kingsmore, S.F., Thompson, J.M., Crockard, A.D., Todd, D., McKirgan, J., Patterson, C., Fay, A.C., McNeill, T.A. Measurement of circulating immune complexes containing IgG, IgM, IgA and IgE by flox cytometry: correlation with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Lab Immunol 1989, 30, 45–52.
Morrow, W.J.W., Isenberg, D.A., Todd-Pokropek, A., Perry, H.F., Snaith, M.L. Useful laboratory measurements in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med 1982, 51, 125–138.
Morrow, W.J.W., Williams, D.J.P., Ferec, C., et al., The use of C3d as a means of monitoring clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1983, 42, 668–671.
Negoro, N., Okamura, M., Takeda, T., Koda, S., Amatsu, K., Inoue, T., Curd, J.G., Kanayama, Y. The clinical significance of iC3b neoantigen expression in plasma from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1989, 32, 1233–1242.
Nürnberger, W., Link, P., Becker, H., Helmke, K., Wahn, V., Dreher, R. Korrelation der C3dg/C3-Ratio zur Krankheitsaktivität beim systemischen lupus erythematosus. Aktuel Rheumatol 1988, 13, 179–182.
Perrin, L.H., Lambert, P.H., Miescher, P.A. Complement breakdown products in plasma from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and patients with membranoproliferative or other glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest 1975, 56, 165–176.
Sekita, K., Doi, T., Muso, E., Yoshida, H., Kanatsu, K., Hamashima, Y. Correlation of C3d fixing circulating immune complexes with disease activity and clinical parameters in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 1984, 55, 487–494.
Stannat, S., Bahlmann, J., Kiessling, D., Koch, K.-M., Deicher, H., Peter, H.H. Complement activation during hemodialysis. Contrib Nephrol 1985, 46, 102–108.
Swaak, A.J., Aarden, L.A., Statius van Eps, L.W., Feltkamp, T.E.W. Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1979, 22, 226–235.
Swaak, A.J., Groenwold, J., Aarden, L.A. Statius van Eps, L.W., Feltkamp, T.E.W. Prognostic value of anti-dsDNA in SLE. Ann Rheum Dis 1982, 41, 388–395.
Swaak, A.J., Groenwold, J., Hannema, A., Hack, C.E. Correlation of disease activity with circulating immune complexes (C1qbA) and complement breakdown products (C3d) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. A prospective study. Rheumatol Int 1985, 5, 215–220.
Tan, E.M., Cohen, A.S., Fries, J.F., Masi, A.T., McShane, D.J., Rothfield, N.F., Schaller, J.G., Talal, N., Winchester, R.J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1982, 25, 1271.
Ter Borg, E.J., Horst, G., Hummel, E.J., Limburg, P.C., Kallenberg, C.G. Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1990, 33, 634–643.
Valentijn, R.M., Van Overhagen, H., Hazevoet, H.M., et al., The value of complement and immune complex determinations in monitoring disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1985, 28, 904–913.
Wild, G., Watkins, J., Ward, A.M., Hughes, P., Hume, A., Rowell, N.R. C4a anaphylatoxin levels as an indicator of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 1990, 80, 167–170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Röther, E., Lang, B., Coldewey, R. et al. Complement split product C3d as an indicator of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 12, 31–35 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02231555
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02231555