Abstract
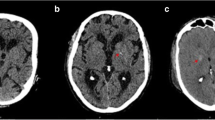
Twenty-two patients aged 36–63 years were diagnosed as having Fahr's syndrome on the basis of the presence on CT of unexpected extensive calcification of the basal ganglia. Even when associated with calcification of other brain areas, the main diagnostic criterion remained basal ganglia calcification larger than 800 mm2. Normal values of parathormone, serum calcium and phosphorus excluded hypercalcaemia and hypoparathyroidism. Mitochondrial CNS disease was excluded clinically. MRI and repeated CT and neurological examination were performed in all of the patients. The patients were divided into two groups: neurologically asymptomatic (group 1) and neurologically symptomatic (group 2). T2-weighted sequences demonstrated hyperintense areas in all of the patients involving the white and the grey matter of the brain. In group 1 the hyperintense lesions were significantly smaller than in group 2. The neurological symptoms correlated better with the hyperintensities on T2-weighted MR images than with the calcification demonstrated on CT. Hyperintensities in T2-weighted MRI and the areas shown by CT to have calcification had different locations. In 15 patients with dementia, the white matter of the entire centrum semiovale was bilaterally hyperintense. In another 3 patients with hemiparesis, hyperintense areas in the internal capsule, contralateral to the side of hemiparesis, were demonstrated in the T2-weighted sequence. The hyperintense T2 signals may reflect a slowly progressive, metabolic or inflammatory process in the brain which subsequently calcifies and are probably responsible for the neurological deficit observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cummings JL, Gosenfeld LF, Houlihan JP, McCaffrey T (1983) Neuropsychiatric disturbances associated with idiopathic calcification of the basal ganglia. Biol Psychiatry 5:591–601
Ducett S, Galle P, Escourolle R, Poirier J, Hauw J (1977) Presence of zinc, aluminium, magnesium in striopallidodentate (SPD) calcifications (Fahr disease): electron probe study. Acta Neuropathol (Barl) 38:7–10
Ellie E, Julien J, Ferrer X (1989) Femilial idiopathic striopallidodentate calcifications. Neurology 39:381–385
Fahr T (1930) Idiopatische Verkalkung der Hirngefässe. Zentralbl Allg Pathol Anat 50:128–133
Harrington MG, Macpherson P, McIntosh WB, Allam BF, Bone I (1982) The significance of the incidental finding of basal ganglia calcification on computed tomography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1168–1170
Henkelman M, Watts JF, Kucharczyk J (1991) High signal intensity in MR images of calcified brain tissue. Radiology 179:199–206
Koller WC, Cochran JW, Klawans KL (1979) Calcification of the basal ganglia: computerized tomography and clinical correlation. Neurology 29: 328–333
Kozik M, Kulczycki J (1978) Laser spectrographic analysis of the cation content in Fahr syndrome. Arch Psychiatr Nervenheilkd 225:135–142
Punvanendran K, Low CH, Tan KP (1982) Basal ganglia calcification of computer tomographic scan. A clinical and radiological correlation. Acta Neurol Scand 6679:309–315
Scotti G, Scialfa G, Tampieri D, Landoni L (1985) MR imaging in Fahr discase. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9: 790–792
Stellamor K, Stellamor V (1983) Comments on radiography of Fahr disease. Roentgen Blatter 36:194–196
Taxer F, Haller R, Konig P (1986) Klinische Frühsymptome und CT-Befunde beim Fahr'schen Syndrom. Nervenarzt 57:583–588
Tofani B, Boudouresques G, Turpin JC, Khalil R (1981) Aspects actuels de la maladie de Fahr. A propos de deux observation de calcifications striopallido-dentelees idiopathiques revelees par la scanographie. Semin Hop Paris 57:1815–1818
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avrahami, E., Cohn, DF., Feibel, M. et al. MRI demonstration and CT correlation of the brain in patients with idiopathic intracerebral calcification. J Neurol 241, 381–384 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02033355
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02033355