Summary
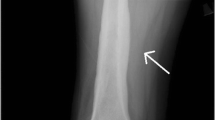
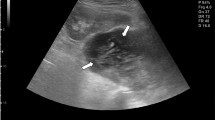
We describe a hypogammaglobulinemic woman with a one-year history of destructive septic osteomyelitis and polyarthritis with positive cultures forUreaplasma urealyticum from joint exudate and blood. The clinical course was complicated by subcutaneous abscesses from which bothU. urealyticum andMycoplasma hominis were grown. Multiple routine cultures had been negative, except for sporadic findings ofStaphylococcus epidermidis before specific cultures for mycoplasmas were performed. Therapy with beta-lactam antibiotics, clindamycin, rifampicin, fusidic acid and aminoglycosides had been given without obvious clinical effect. Intravenous doxycycline treatment instituted after microbiological diagnosis had a dramatic effect on the clinical course. The clinical suspicion of mycoplasma and ureaplasma as etiologic agents of orthopaedic infections in hypogammaglobulinemic patients is mandatory in order to perform appropriate cultures.
Zusammenfassung
Wir beschreiben den Fall einer destruktiven Osteomyelitis und Polyarthritis bei einer Frau mit Hypogammaglobulinämie; aus Gelenkexsudat und Blut wurdeUreaplasma urealyticum isoliert; der Krankheitsverlauf zog sich über ein Jahr hin. Als Komplikation traten subkutane Abszesse auf, aus denenU. urealyticum undMycoplasma hominis gezüchtet wurden. Routinekulturen waren wiederholt negativ; bevor spezifische Kulturen für Mykoplasmen angelegt wurden, fand sich sporadischStaphylococcus epidermidis. Therapieversuche mit Betalactam-Antibiotika, Clindamycin, Rifampicin, Fusidinsäure und Aminoglykosiden waren ohne eindeutige klinische Wirkung. Der klinische Verlauf nahm eine dramatische Wende, als nach mikrobiologischer Erregerdiagnostik eine intravenöse Therapie mit Doxycyclin eingeleitet worden war. Bei Knochen- und Gelenkinfektionen, die bei Patienten mit Hypogammaglobulinämie auftreten, muß der Kliniker an eine Mykoplasma- und Ureaplasma-Ätiologie denken, um die entsprechenden kulturellen Untersuchungen zu veranlassen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webster, D., Taylor-Robinson, D., Furr, P., Asherson, G. Mycoplasma (ureaplasma) septic arthritis in hypogammaglobulinemia. Br. Med. J. 1 (1978), 478–479.
Stuckey, M., Quinn, P., Gelfand, E. Identification ofUreaplasma urealyticum (T-strain mycoplasma) in patient with polyarthritis. Lancet ii (1978) 917–920.
Vogler, L., Waites, K., Wright, P., Perrin, J., Cassell, G. Ureaplasma urealyticum polyarthritis in agammaglobulinemia. Ped. Infect. Dis. 4 (1985) 687–691.
Andrews, B., Robertson, J., Stanbridge, E., de la Maza, L., Hoffer, M., Cesario, T. Ureaplasma urealyticum polyarthritis with common variable immunodeficiency. Arthritis and Rheumatism 29 (1986) 31.
Kraus, V., Baraniuk, V., Hill, G., Bates, W. Ureaplasma urealyticum septic arthritis in hypogammaglobulinemia. J. Rheumatol. 15 (1988) 369–371.
Madoff, S., Hooper, D. Nongenitourinary infections caused byMycoplasma hominis in adults. Rev. Infect. Dis. 10 (1988) 602–613.
Taylor-Robinson, D., Gumpel, J., Hill, A., Swannell, S. Isolation ofMycoplasma pneumoniae from the synovial fluid of a hypogammaglobulinemic patient in a survey of patients with inflammatory polyarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 37 (1978) 180–182.
Johnston, C., Webster, D., Taylor-Robinson, D., Rapaport, G., Hughes, G. Primary late onset hypogammaglobulinemia associated with inflammatory polyarthritis and septic arthritis due toMycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 42 (1983) 108–110.
Roifman, C., Pandu Rao, C., Lederman, H., Lavi, S., Quinn, P., Gelfand, E. Increased susceptibility to mycoplasma infection in patients with hypogammaglobulinemia. Am. J. Med. 80 (1986) 590–594.
So, A., Furr, P., Taylor-Robinson, D. Arthritis caused byMycoplasma salivarium in hypogammaglobulinemia. Br. Med. J. 286 (1983) 762–763.
Shepard, M., Lunceford, C. Differential agar medium (A 7) for identification ofUreaplasma urealyticum (human T mycoplasmas) in primary cultures of clinical material. J. Clin. Microbiol. 3 (1976) 613–625.
Rosendal, S., Black, F. Direct and indirect immunofluorescence of unfixed and fixed mycoplasma colonies. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. Sect. B 80 (1972) 615–622.
Clyde, W. Jr. Serological identification of mycoplasmas from humans. In:Tully, J., Razin, S. (eds. Methods in mycoplasmology, Vol. 2. Academic Press, N. Y. 1983, pp. 37–45.
Rylander, M., Hallander, H. In vitro comparison of the activity of doxycycline, tetracycline, erythromycin and a new macrolide, CP 62993, againstMycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycoplasma hominis andUreaplasma urealyticum. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. Suppl. 53 (1988) 12–17.
Good, R., Rotstein, J. Rheumatoid arthritis and agammaglobulinemia. Bull. Rheum. Dis. 10 (1960) 203.
Hansel, T., Haeney, M., Thompson, R. Primary hypogammaglobulinemia and arthritis. Br. Med. J. 295 (1987) 174–175.
Webster, A., Furr, P., Hughes-Jones, N., Gorick, B., Taylor-Robinson, D. Critical dependence on antibody for defence against mycoplasmas. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 71 (1988) 383–387.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jorup-Rönström, C., Ahl, T., Hammarström, L. et al. Septic osteomyelitis and polyarthritis with ureaplasma in hypogammaglobulinemia. Infection 17, 301–303 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650712
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650712