Abstract
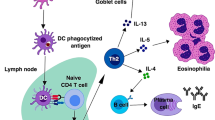
Evidence is accumulating to suggest the existence of polarized human T-cell responses, reminiscent of TH1 and TH2 subsets described for mouse T cells. Human TH1 cells preferentially develop during infections by intracellular bacteria and trigger phagocyte-mediated host defense, whereas TH2 cells, which predominate during helminthic infestations and in response to common environmental allergens, are responsible for phagocyte-independent host response. Human TH1 and TH2 cells exhibit not only different functional properties but probably also distinct surface markers; TH2, but not TH1, clones express membrane CD30 and release the soluble form of CD30, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily. The cytokine profile of “natural immunity” evoked by different offending agents in the context of different host genetic backgrounds appears to be the most critical factor in determining the phenotype of the subsequent specific response. IL-12 and IFN-α and γ produced by macrophages and NK cells favor the development of TH1 cells, whereas the early production of IL-4 by a stillunidentified cell type favors the development of TH2 cells. Clearly, polarized human TH1 and TH2 responses not only play different roles in protection, they can also promote different immunopathological reactions. Strong and persistent TH1 responses seen to be involved in organ-specific autoimmunity, contact dermatitis, and some chronic inflammatory disorders of unknown etiology. In contrast, polarized TH2 responses favor a reduced protection against the majority of infectious agents (including HIV) and, in genetically predisposed hosts, are responsible for triggering of allergic atopic disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mosmann TR, Chervinshi H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL: Two types of murine helper T-cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol 136:2348–2357, 1986
Mosmann TR, Coffman RL: TH1 and TH2 Cells: Different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol 7:145–173, 1989
Street NE, Schumacher JH, Fong TAT, Bass H, Fiorentino DF, Leverah A, Mosmann TR: Heterogeneity of mouse helper T cells: Evidence from bulk cultures and limiting dilution cloning for precursors of TH1 and TH2 cells. J Immunol 144:1629–1639, 1990
Ani S: Allergen- and bacterial antigen-specific t-cell clones established from atopic donors show a different profile of cytokine production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4538–4542, 1991
Del Prete GF, De Carli M, Mastromauro C, Macchia D, Biagiotti R, Ricci M, Romagnani S: Purified protein derivative ofMycobacterium tuberculosis and excretory-secretory antigen(s) ofToxocara cams expandin vitro human t cells with stable and opposite (type 1 T helper to type 2 T helper) profile of cytokine production. J Clin Invest 88:346–350, 1991
Maggi E, Biswas P, Del Prete GF, Parronchi P, Macchia D, Simonelli C, Emmi L, De Carli M, Tiri A, Ricci M, Romagnani S: Accumulation of TH2-like helper T cells in the conjunctiva of patients with vernal conjunctivitis. J Immunol 146:1169–1174, 1991
Del Prete GF, Del Carli M, D'Elios MM, Maestrelli P, Ricci M, Fabbri L, Romagnani S: Allergen exposure induces the activation of allergen-specific TH2 cells in the airway mucosa of patients with allergic respiratory disorders. Eur J Immunol 23:1445–1449, 1993
Romagnani S: Lymphokine production by human T cells in disease states. Annu Rev Immunol 12:227–257, 1994
van der Heijden FL, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, Kapsenberg ML: High frequency of IL-4-producing CD4+ allergen-specific T lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis lesional skin. J Invest Dermatol 97:389–394, 1991
van Reijsen FC, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CAFM, Kalthoff FS, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Westland JKT, Mudde GC: Skin derived aeroallergen-specific T-cell clones of TH2 phenotype in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 90:184–192, 1992
Salgame P, Abrams JS, Clayberger C, Goldstein H, Convitt J, Modlin RL, Bloom BR: Differing lymphokine profiles and functional subsets of human CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell clones. Science 254:279–281, 1991
Kapsenberg ML, Wierenga EA, Bos JD, Jansen HM: Functional subsets of allergen-reactivehuman CD4+ T cells. Immunol Today 12:392–395, 1991
Brod SA, Benjamin D, Hafler DA: Restricted T cell expression of IL-2/TFN-γ mRNA in human inflammatory diseases. J Immunol 147:810–815, 1991
Yssel H, Shanafelt MC, Soderberg C, Schneider PV, Anzola J, Peltz G: Borrelia burgdorferi activates a T helper type 1-like T cell subset in Lyme arthritis. J Exp Med 174:593–601, 1991
Schlaak J, Hermann E, Ringhoffer M, Probst P, Gallati H, Meyer zum Buschenfeld K-H, Fleischer B: Predominance of TH1-type T cells in synvial fluid of patients withYersinia enterocolitica reactive arthritis. Eur J Immunol 22:2771–2776, 1992
Hamid Q, Azzawi M, Ying S, Moqbel R, Wardlaw AJ, Corrigan CJ, Bradley B, Durham SR, Collins JV, Jeffery PK, Quint DJ, Kay AB: Expression of mRNA for interleukin-5 in mucosal bronchial biopsies from asthma. J Clin Invest 87:1541–1546, 1991
Robinson DS, Hamid Q, Ying S, Tsicopoulos A, Barkans J, Bentley AM, Corrigan CJ, Durham SR, Kay AB: Predominant TH2-like bronchoalveolar T-lymphocyte population in atopic asthma. N Engl J Med 326:295–304, 1992
Selmaj K, Raine CS, Cannella B, Brosnan CF: Identification of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Clin Invest 87:949–954, 1991
Foulis AK, McGil M, Farquharson, MA: Insulitis in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in man—macrophages, lymphocytes, and interferon-γ containing cells. J Pathol 165:97–102, 1991
Schandene L, Ferster A, Mascart-Lemone F, Crusiaux A, Gerard C, Marchant A, Lybin M, Velu T, Sariban E, Goldman M: T helper type 2-like cells and therapeutic effects of interferon-γ in combined immunodeficiency with hypereosoniphilia (Ommenn's syndrome). Eur J Immunol 23:56–60, 1993
Field EH, Noelle RJ, Rouse T, Goeken J, Waldschmidt T: Evidence for excessive TH2 CD4+ subset activityin vivo. J Immunol 151:48–59, 1991
Cogan E, Schandane L, Crusiaux A, Cochaux P, Velu T, Goldman M: A TH2 Clonal disease presenting as hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med 330:535–538, 1994
Del Prete GF, De Carli M, Almerigogna F, Giudizi MG, Biagiotti R, Romagnani S: Human IL-10 is produced by both type 1 helper (TH1) and type 2 helper (TH2) T cell clones and inhibits their antigen-specific proliferation and cytokine production. J Immunol 150:1–8, 1993
Romagnani S: TH1 and TH2 subsets of CD4+ T lymphocytes. Sci Am Sic Med 1:68–77, 1994
Romagnani S: Human TH1 and TH2 subsets: “Eppur si muove!” Eur Cyt Netw 5:7–12, 1994
Del Prete GF, De Carli M, Ricci M, Romagnani S: Helper activity for immunoglobulin synthesis of TH1 and TH2 human T cell clones: The help of TH1 clones is limited by their cytolytic capacity. J Exp Med 174:809–813, 1991
Romagnani S: Human TH1 and TH2: Doubt no more. Immunol Today 12:256–257, 199
Del Prete GF, De Carli M, Lammel R, D'Elios MM, Daniel KC, Giusti B, Abbate R, Romagnani S: TH1 and TH2 T helper cells exert opposite regulatory effects on procoagulant activity and tissue factor production by human monocytes. Blood, 1985 (in press)
Smith C, Davis T, Anderson D, Solam L, Beckmann MP, Jerzy R, Dower SK, Cosman D, Goodwin RG: A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science 248:1019–1023, 1990
Smith CA, Gruss H-J, Davis T, Anderson D, Farrah T, Baker E, Sutherland GR, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Grabstein KH, Gliniak B, McAlister IB, Fanslow W, Alderson M, Falk B, Gimpel S, Gillis S, Din WS, Goodwin RG, Armitage RJ: CD30 antigen, a marker for Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a receptor whose ligand defines an emerging family of cytokines with homology to TNF. Cell 73:1349–1360, 1993
Schwab U, Stein H, Gerde J, Lemke H, Kirchner H, Schaadt M, Diehl V: Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin's and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature 299:65–67, 1982
Stein H, Mason DY, Gerdes J, O'Connor N, Wainscoat J, Pallesen G, Gatter K, Falini B, Delson G, Lemke H, Schwarting R, Lennert K: The expression of Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: Evidence that the Reed Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood 66:848–858, 1985
Andreesen R, Osterholz J, Lohr GW, Bross KJ: A Hodgkin cell-specific antigen is expressed on a subset of auto- and alloactivated T (helper) lymphoblasts. Blood 63:1299–1302, 1984
Ellis TM, Simms PE, Slivnick DJ, Jack H-M, Fisher RI: CD30 is signal-transducing molecule that defines a subset of human activated CD45RO+ T cells. J Immunol 151:2380–2389, 1993
Del Prete GF, De Carli M, Almerigogna F, Daniel CK, D'Elios MM, Zancuoghi G, Vinante F, Pizzolo G, Romagnani S: Preferential expression of CD30 by human CD4+ T cells producing TH2-type cytokines. FASEB J. 9:81–86, 1995
Manetti R, Annuziato F, Biagiotti R, Giudizi MG, Piccinni MP, Giannarini L, Sampognaro S, Parronchi P, Vinante F, Pizzolo G, Maggi E, Romagnani S: CD30 expression by CD8+ T cells producing TH2-type cytokines. Evidence for large numbers of CD8+CD30+ T cell clones in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection J. Exp. Red. 180:2407–2412, 1994
Maggi E, Giudizi MG, Biagiotti R, Annunziato F, Manetti R, Piccinni MP, Parronchi P, Sampognaro S, Giannarini L, Zuccati G, Romagnani S: TH2-like CD8+ T cells showing B cell helper function and reduced cytolytic activity in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Exp Med 180:489–496, 1994
Swain SL: IL-4 dictates T-cell differentiation. Res Immunol 144:616–620, 1993
Seder RA, Paul WE, Davis MM, Fazekas de St Groth B: The presence of interleukin 4 duringin vitro priming determines the lymphocyte-producing potential of CD4+ T cells from T cell receptor transgenic mice. J Exp Med 176:1091–1098, 1992
Hsieh C-S, Heimberger AB, Gold JS, O'Garra A, Murphy KS: Differential regulation of T helper phenotype development by IL-4 and IL-10 in an αβ-transgenic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6065–6069, 1992
Williams ME, Change TL, Burke SK, Lichtman AH, Abbas AK: Activation of functionally distinct subsets of Cd4+ T lymphocytes. Res Immunol 142:23–27, 1991
Magilavy DB, Fitch FW, Gajewski TF: Murine hepatic accessory cells support the proliferation of TH1 but not TH2 helper T cell clones. J Exp Med 170:985–990, 1989
Schmitz J, Assenmacher M, Radbruch A: Induction of cellular immunity: Macrophages are the principal antigen-presenting cells for TH calls secreting IFN-γ (TH1 cells).In New Advances on Cytokines, S Romagnani, TR Mosmann, AK Abbas (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1992, pp 131–136
Williams IR, Unanue ER: Costimulatory requirements of murine TH1 clones. The role of accessory cell-derived signals in responses to anti-CD3 antibody. J Immunol 145:85–93, 1990
Daynes RA, Meikle AW, Araneo BA: Locally active steroid hormones may facilitate compartmentalzation of immunity by regulating the types of lymphokines produced by helper T cells. Res Immunol 142:40–44, 1991
Rook GAW, Hernandez-Pando R, Lightman SL: Hormones, peripherally activated phrohormones and regulation of the TH1/TH2 Balance. Immunol Today 15:301–303, 1994
Gajewski TF, Joyce J, Fitch FW: Anti-proliferative effect of IFN-γ in immune regulation. III. Differential selection of TH1 and TH2 murine helper T lymphocyte clones using recombinant IL-2 and recombinant IFN-γ. J Immunol 143:15–22, 1989
Scott P, Pearce E, Cheever AW, Coffman RL and Sher A: Role of cytokines and CD4+ T-cell subsets in the regulation of parasite immunity and disease. Immunol Rev 112:161–182, 1989
Heinzel FP, Sadick MD, Holaday BJ, Coffman RL, Locksley RM: Reciprocal expression of interferon gamma or IL-4 during the resolution or progression of murine leishmaniasis. Evidence for expansion of distinct helper T cell subsets. J Exp Med 169:59–67, 1989
Hsieh C-S, Macatonia SE, Tripp CS, Wolf SF, O'Garra A, Murphy KM: Development of TH1 CD4+ T Cells through IL-12 produced byListeria induced macrophages. Science 260:547–549, 1993
Wegmann TG, Lin H, Guilbert L, Mosmann TR: Bidirectional cytokine interactions in the maternal-fetal relationship: Is successful pregnancy a TH2 phenomenon? Immunol Today 14:353–356, 1993
Gross A, Ben-Sasson Z, Paul WE: Anti-IL-4 diminishesin vivo priming for antigen-specific IL-4 production by T cells. J Immunol 150:2112–2120, 1993
Romagnani S: Induction of TH1 and TH2 Response: A key role for the natural immune response? Immunol Today 13:379–380, 1992
Maggi E, Parronchi P, Manetti R, Simonelli C, Piccinni MP, Santoni-Rugiu F, De Carli M, Ricci M, Romagnani S: Reciprocal regulatory role of IFN-γ and IL-4 on thein vitro development of TH1 and TH2 clones. J Immunol 148:2142–2147, 1992
Parronchi P, De Carli M, Manetti R, Simonelli C, Sampognaro S, Piccinni MP, Macchia D, Maggi E, Del Prete GF, Romagnani S: IL-4 and IFNs (alpha and gamma) exert opposite regulatory effects on the development of cytolytic potential by TH1 or TH2 human T cell clones. J Immunol 149:2977–2984, 1992
Manetti R, Barak V, Piccinni M-P, Sampognaro S, Parronchi P, Maggi E, Dinarello CA, Romagnani S: Interleukin 1 favors thein vitro development of type 2 helper (TH2) human T cell clones. Res Immunol 145:93–100, 1994
Manetti R, Parronchi P, Giudizi M-G, Piccinni M-P, Maggi E, Trinchieri G, Romagnani S: Natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12) induces T helper type 1 (TH1)-specific immune responses and inhibits the development of IL-4-producting TH cells. J Exp Med 177:1199–1204, 1993
Piccinni M-P, Giudizi M-G, Biagiotti R, Annunziato F, Manetti R, Giannarini L, Parronchi P, Sampognaro S, Maggi E, Romagnani S: Progesterone favors the development of human T helper (TH) cells producing TH2-type cytokines and promotes both IL-4 production and membrane CD30 expression in established TH1 clones. J. Immunol. 1995 (in press)
Manetti R, Gerosa F, Giudizi M-G, Biagiotti R, Parronchi P, Piccinni M-P, Sampognaro S, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Trinchieri G: Interleukin-12 induces stable priming for interferon-g (IFN-g) production during differentiation of human T helper (TH) cells and transient IFN-γ production in established TH2 cells clones. J Exp Med 179:1273–1283, 1994
De Carli M, Berthold S, Fickenscher H, Fleckestein IM, D;Elios MM, Gao Q, Biagiotti R, Giudizi MG, Kalden JR, Fleckenstein B, Romagnani S, Del Prete GF: Immortalization with herpes virus saimiri modulates the cytokine secretion profile of established TH1 and TH2 human T cell clones. J Immunol 151:5022–5030, 1993
Secrist H, Chelen CJ, Wen Y, Marshall JD, Umetsu DT: Allergen immunotherapy decreases interleukin 4 production in CD4+ T cells from allergic individuals. J Exp Med 178:2123–2130, 1993
Zlotnik A, Bean AGD: Production of IL-4 by non-TH2 T cell subsets: Possible role of CD4−CD8−ab TCR+ and CD4 subset T cells in T helper subset regulation. Res Immunol 144:606–609, 1993
Yashimoto T, Paul WE: CD4pos, NKl.lpos T cells promptly produce interleukin 4 in response toin vivo challenge with anti-CD3. J Exp Med 179:1285–1295, 1994
Piccinni MP, Macchia D, Parronchi P, Ciudizi M-G, Bani D, Alterini R, Grossi A, Ricci M, Maggie E, Romagnani S: Human bone marrow non-B, non-T cells produce interleukin 4 in response to cross-linkage of Fcε and Fcγ receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8656–8660, 1991
Bradding P, Feather IH, Howarth PH, Mueller R, Roberts JA, Britten K, Bews JPA, Hunt TC, Okayama Y, Heusser CH, Bullock GR, Church MK, Holgate ST: Interleukin 4 is localized and released by human mast cells. J Exp Med 176:1381–1386, 1992
Brunner T, Heusser CI, Dahinden CA: Human peripheral blood basophils primed by interleukin-3 (IL-3) produce IL-4 in response to immunoglobulin E receptor stimulation. J Exp Med 177:605–612, 1993
Marsh DG, Neely JD, Breazeale DR, Ghosh B, Freidhoff LR, Ehrlich-Kautzky E, Schou C, Krishnaswamy G, Beaty TH: Linkage analysis of IL-4 and other chromosome 5q31.1 markers and total serum immunoglobulin E concentrations. Science 264:1152–1156, 1994
Chehimi J, Starr SE, Frank I, D'Andrea A, MacGregor RR: Impaired interleukin-12 production in HIV-infected patients. J Exp Med 179:1361–1366, 1994
Clerici M, Sherer GM: A TH1 to TH2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today 14:107–111, 1993
Maggi E, Mazzetti M, Ravina A, Manetti R, De Carli M, Annunziato F, Piccinni MP, Carbonari M, Pesce AM, Del Prete G, Romagnani S: Ability of HIV to promote a TH1 to TH0 shift and to replicate preferentially in TH2 and TH0 cells. Science 265:244–248, 1994
Maggi E, Manetti R, Annunziato F, Biagiotti R, Giudizi MG, Ravina A, Almerigogna F, Boiani N, Alderson M, Romagnani S: Activation of HIV expression by CD30 triggering in CDU+ T cells (submitted)
Khoury SJ, Hancock WW, Weiner HL: Oral tolerance to myelic basic protein and natural recovery from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis are associated with downregulation of inflammatory cytokines and differential upregulation of transforming growth factor b, interleukin 4, and prostaglandin E expression in the brain. J Exp Med 176:1355–1365, 1992
Campbell I, Kay TW, Oxbrow L, Harrison LC: Essential role for Interferon-γ and interleukin-6 in autoimmune insulin-dependent diabetes in NOD/Wehi mice. J Clin Invest 87:739–745, 1991
Mills JA: Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 330:1871–1879, 1994
Goldman M, Druet P, Gleichmann E: TH2 cells in systemic autoimmunity: Insights from allogeneic diseases and chemicallyinduced autoimmunity. Immunol Today 12:223–227, 1991
Circulating levels of soluble CD30, a marker of cells producing TH2-type cytokines, are incresed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and correlate with disease activity. Clin. Exp. Rheum. 1995 (in press)
Romagnani S: Regulation of TH2 development in allergy. Curr Opin Immunol 6:838–846, 1994